Sternocleidomastoid This large neck muscle helps rotate the head upward and side to side The muscles of the face overlap and crisscross over Human Anatomy Muscles back of the head and the neck So many muscles that cause migraines, arm, neck, shoulders, and back pain Human Anatomy Muscles back of the head and the neck Today Explore When autocomplete results are available use up and down arrows to review and enter to select Touch device users The neck refers to the collection of structures that connect the head to the torso It is a complex structure composed of many bones, muscles, nerves, blood vessels, lymphatics, and other connective tissues The cervical spine is the bony part of the neck Its primary function is to provide support for the skull, while still allowing for movement It is the most flexible part of the
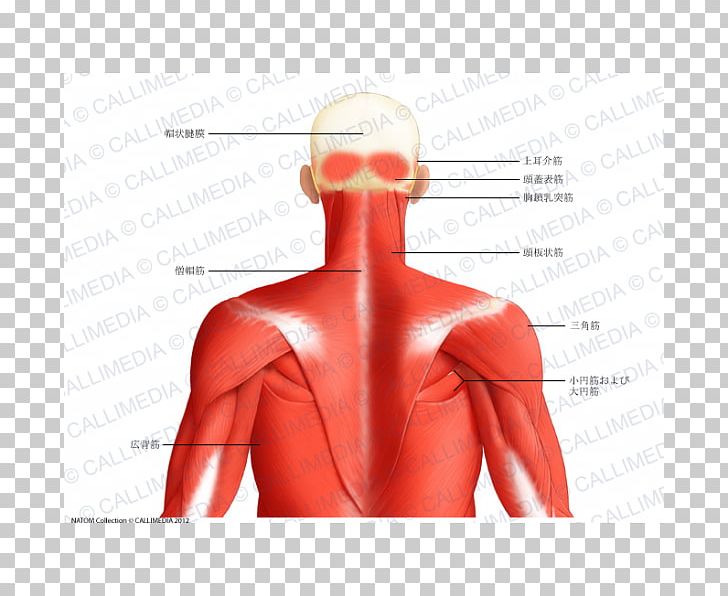
Muscle Posterior Triangle Of The Neck Head And Neck Anatomy Human Body Trapezius Png Clipart Abdomen
Back of head muscle anatomy
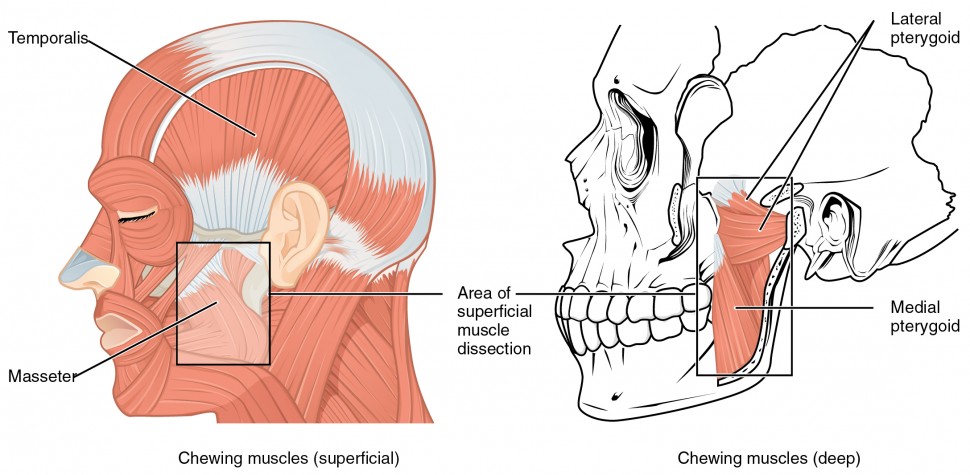
Back of head muscle anatomy-The four muscles masseters, temporalis, medial pterygoid and lateral pterygoid are associated with jaw movements receiving motor innervation from the mandibular nerve (CNV3) In this section, learn more about the muscles of the head the tongue, muscles of facial expression, extraocular muscles and muscles of masticationThe anatomy of the head and neck of the human body, including the bones, muscles, blood vessels, nerves, glands, nose, mouth, and throat Head & Neck Anatomy 19 3D model by INTERVOKE (@intervoke)
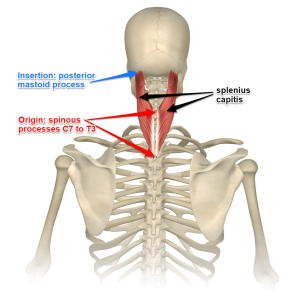



Understanding The Spinotransversales The Superficial Intrinsic Muscles Of The Back
The muscles of the chest and upper back occupy the thoracic region of the body inferior to the neck and superior to the abdominal region and include the muscles of the shoulders These important muscles control many motions that involve moving the arms and head – such as throwing a ball, looking up at the sky, and raising your hand Muscles of the Low Back and Pelvis – posterior superficial view Muscles of the Low Back and Pelvis – right lateral deep view Muscles of the Low Back and Pelvis –Head Muscles Anatomy By Stepan Ayvazyan The muscles of the head are divided into two large groups – the mimic muscles and the muscles of mastication The main functions of the mimic muscles are the transmission of emotions through facial expressions, as well as participation in defensive reactions, such as blinking or sneezing
Skin anatomy is often more complex than people think In other words, having a thick skull isn't necessarily a bad thing On this page, you'll find links to descriptions and pictures of the human b The sternum or breastbone sits in the center of the ribcage Muscles originate from the sternum, including those that move the neck, head, and armsThe semispinalis capitis, splenius capitis, and longissimus capitis muscles all help the head extend toward the back They also work with sternocleidomastoid muscles to rotate the head left and right After working on the computer with their head bent forward, a person might feel soreness in these musclesThe short head, arises from the lateral lip of the linea aspera, between the adductor magnus and vastus lateralis
The occipital glands (lymphoglandulæ occipitales), one to three in nu ber, are placed on the back of the head close to the margin of the Trapezius and resting on the insertion of the Semispinalis capitisTheir afferent vessels drain the occipital region of the scalp, while their efferents pass to the superior deep cervical glands The posterior auricular glands (lymphoglandulæ auriculares Back Of Skull Anatomy / Back Of The Head Muscle Structure And Nerve System Diagram Stock Vector Illustration Of Labeled Muscle The skull is a bony structure that supports the face and forms a protective cavity for the brain The skull base is the inferior portion of the neurocranium Learn how they work and how to exercise them Paraspinal muscles are those long back muscles that sometimes get ropy The semispinalis muscle is a type of transversospinalis muscle found in the human body The spine provides support to hold the head and body up straight The semispinalis muscle is the most superficial
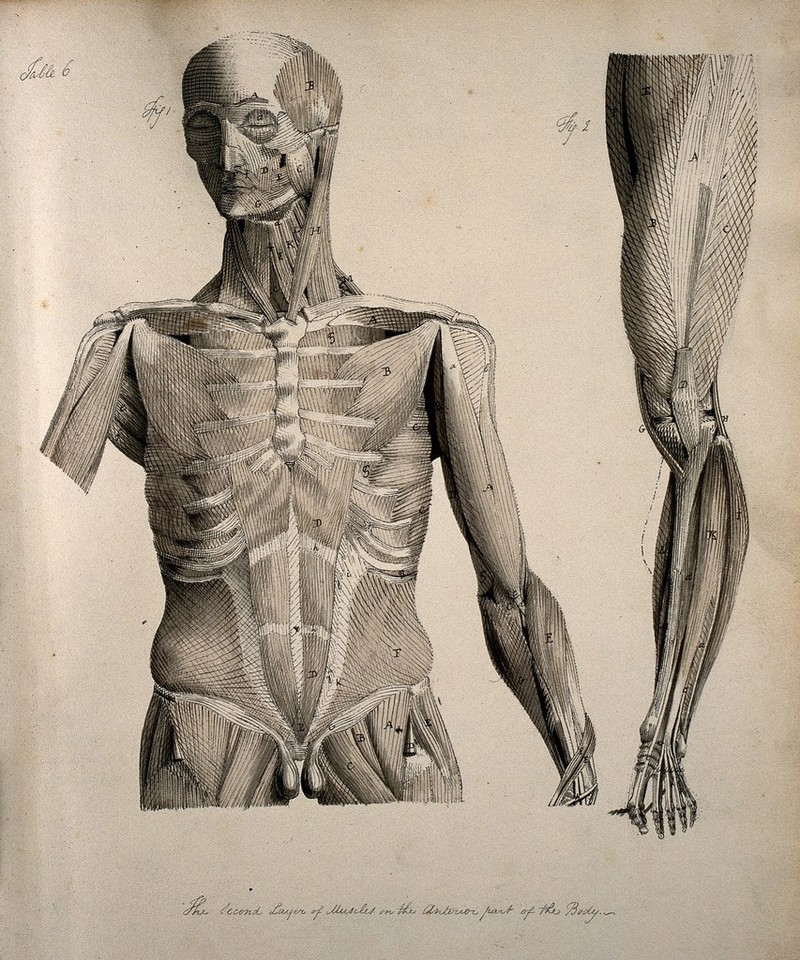



Left Muscles Of The Head And Trunk Front View Right Muscles Of The Thigh And Leg Front View Coloured Drawing 18 Wellcome Collection




Back Of Head Anatomy Muscles Manual
These muscles are able to move the upper limb as they originate at the vertebral column and insert onto either the clavicle, scapula or humerus Whilst the superficial muscles of the back allow movements at the shoulder, the intermediate muscles of the back work to elevate and depress the rib cage There are two major muscles within this category – the serratus posterior superior andMuscles of the Back Region Listed Alphabetically;The muscles of the head can be grouped into two categories the muscles of mastication (masticatory muscles), which are derivatives of the first pharyngeal arch, and the muscles of facial expression (facial muscles), which are derivatives of the second pharyngeal arch Because of their different embryological development the two groups of head muscles are supplied by two



Neck Muscles Pain




David Weinstock Nkt On Instagram My New Client Was Referred To Me By My Friend The Dentist For Tmjd Or Human Body Anatomy Head Muscles Human Muscle Anatomy
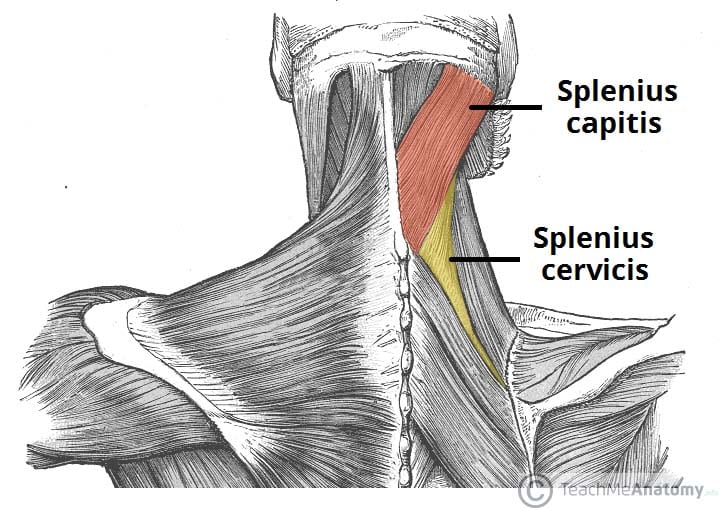
In this video lesson, you will discover the main muscles of the head, neck and shoulders Muscles of the Head The forehead is covered by a flat and wide muscle, called the frontalis In fact, it is the front portion of quite a large muscle that covers the entire top and back section of the skullMuscles That Move the Head, 2 Trunk Muscles, 2 Muscles of the Thorax, 2 Muscles of the Abdominal Wall, 2 Muscles of the Back, 290 Muscles of the Pelvic Floor, 290 Upper Limb Muscles, 293 Muscles Acting on the Shoulder Girdle, 293 and most muscles funcLEVER SYSTEMS lever Anatomy of the Muscular System Chapter 10 D A,The splenius capitis muscle is a broad, strap like muscle located in the back of the neck It connects the base of the skull to the vertebrae in the neck and upper thorax When one muscle acts singly, it causes the head to rotate and bend toward one side;




Back Muscles Anatomy Of Upper Middle Lower Back Pain In Diagrams Goodpath




Human Anatomy Showing Back Full Body Stock Photo Download Image Now Istock
Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation Artery Notes Image; Splenius capitis Located in the back of the neck, it helps the erection of the head as well as extension, sidetoside movement, and rotation of the head and neck to one side Longissimus capitis It allows rotation reflex of head to one side, and is part of the intermediate column of the muscle group sacrospinalis that runs along the neck and This example from Gray's Anatomy shows the cartilages of the throat and the surface anatomy of the neck, with the prominent Sternocleidomastoideus which is often thrown into sharp relief when the head is turned or tilted It terminates toward the




Pin By Carol Knop On Anatomy Neck Muscle Anatomy Human Muscle Anatomy Anatomy




Anatomy Anatomy Massage Therapy Migraine
3 rows Back muscles The back muscles are anatomically layered into superficial (extrinsic) and In addition to housing main parts of the nervous system — the brain and spine — and the start of the digestive system, the head contains many important sensory organs The muscles of the back categorize into three groups The intrinsic or deep muscles are those muscles that fuse with the vertebral column The second group is the superficial muscles, which help with shoulder and neck movements The final group is the intermediate muscles, which help with the movement of the thoracic cage Only the intrinsic muscles are



The 6 Best Muscles To Self Massage For Instant Relief Of Neck And Upper Back Tension Head To Toe Muscle Clinic




Human Anatomy Showing Face Head Shoulders And Back Stock Photo Download Image Now Istock
Structure It has two heads of origin the long head arises from the lower and inner impression on the posterior part of the tuberosity of the ischiumThis is a common tendon origin with the semitendinosus muscle, and from the lower part of the sacrotuberous ligament;Equally important is the erector spinae muscles The muscle has a frontal belly and an occipital (near the occipital bone on the posterior part of the skull) belly In other words, there is a muscle on the forehead (frontalis) and one on the back of the head (occipitalis), but there is no muscle across the top of the head
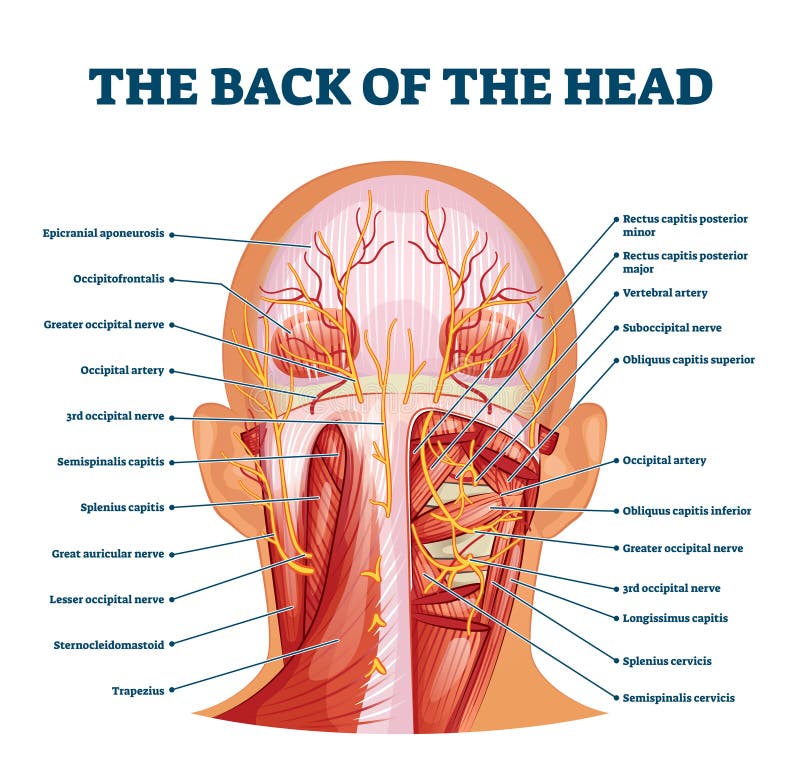



Back Of The Head Muscle Structure And Nerve System Diagram Stock Vector Illustration Of Labeled Muscle




Facial Muscle Anatomy With Audio And For Notes Muscle Diagram Head Muscles Forearm Muscle Anatomy
The neck muscles, including the sternocleidomastoid and the trapezius, are responsible for the gross motor movement in the muscular system of the head and neck They move the head in every direction, pulling the skull and jaw towards the shoulders, spine, and scapula Back Of Neck Anatomy Diagram / Human Head Back Side Female Head Muscles Anatomy Back View The neck also protects the nerves and the spinal cord as well to help maintain a healthy neck anatomy area diagram body maps Find out more about your back here! The muscles of the neck run from the base of the skull to the upper back and work together to bend the head and assist in breathing It is also flexible enough to prevent injury and a He is an attending emergency medicine phys Find out
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/male-musculature--artwork-147218800-cb22d819dc434b75bb6f4bf020e9ed8c.jpg)



Sternocleidomastoid Muscle Anatomy And Function




Nerves And Muscles Of The Head Illustration Stock Image F029 6986 Science Photo Library
Human muscle system, the muscles of the human body that work the skeletal system, that are under voluntary control, and that are concerned with movement, posture, and balance Broadly considered, human muscle—like the muscles of all vertebrates—is often divided into striated muscle, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle Morgan Raimondo Bovine anatomy Illustrated atlas This module of vetAnatomy provides the basics on the anatomy of the bull for students of veterinary medicine This veterinary anatomical atlas includes 27 scientific illustrations with a selection of labelled structures to understand and discover animal anatomy (skeleton, bones, muscles, joints and viscera)Together, these muscles bring the head into an upright position




Muscles Of The Neck And Torso Classic Human Anatomy In Motion The Artist S Guide To The Dynamics Of Figure Drawing
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12652/Introduction.png)



Nerves And Arteries Of Head And Neck Anatomy Branches Kenhub
13,271 anatomy of the head and neck stock photos, vectors, and illustrations are available royaltyfree See anatomy of the head and neck stock video clips of 133 muscle head anatomy vocal organ diagram female neck anatomy neck wireframe head neck human anatomy head artery anatomy face pharynx vector neck degree head anatomy 3d Human head (anterior view) The human head is more than just a nuisance responsible for your headaches It is a complex anatomical structure weighing up to five kilograms that rests on the bony skull and in turn, the neckIn addition to the evident ears, eyes, nose, and mouth, the head supports a variety of other important structures Muscles of masticationErector spinae iliac crest, sacrum, transverse and spinous processes of vertebrae and supraspinal ligament angles of the ribs, transverse and spinous processes of vertebrae, posterior aspect of the skull extends and laterally




3d Illustration Of Female Head Muscles Anatomy Back View Stock Illustration Illustration Of Health Face
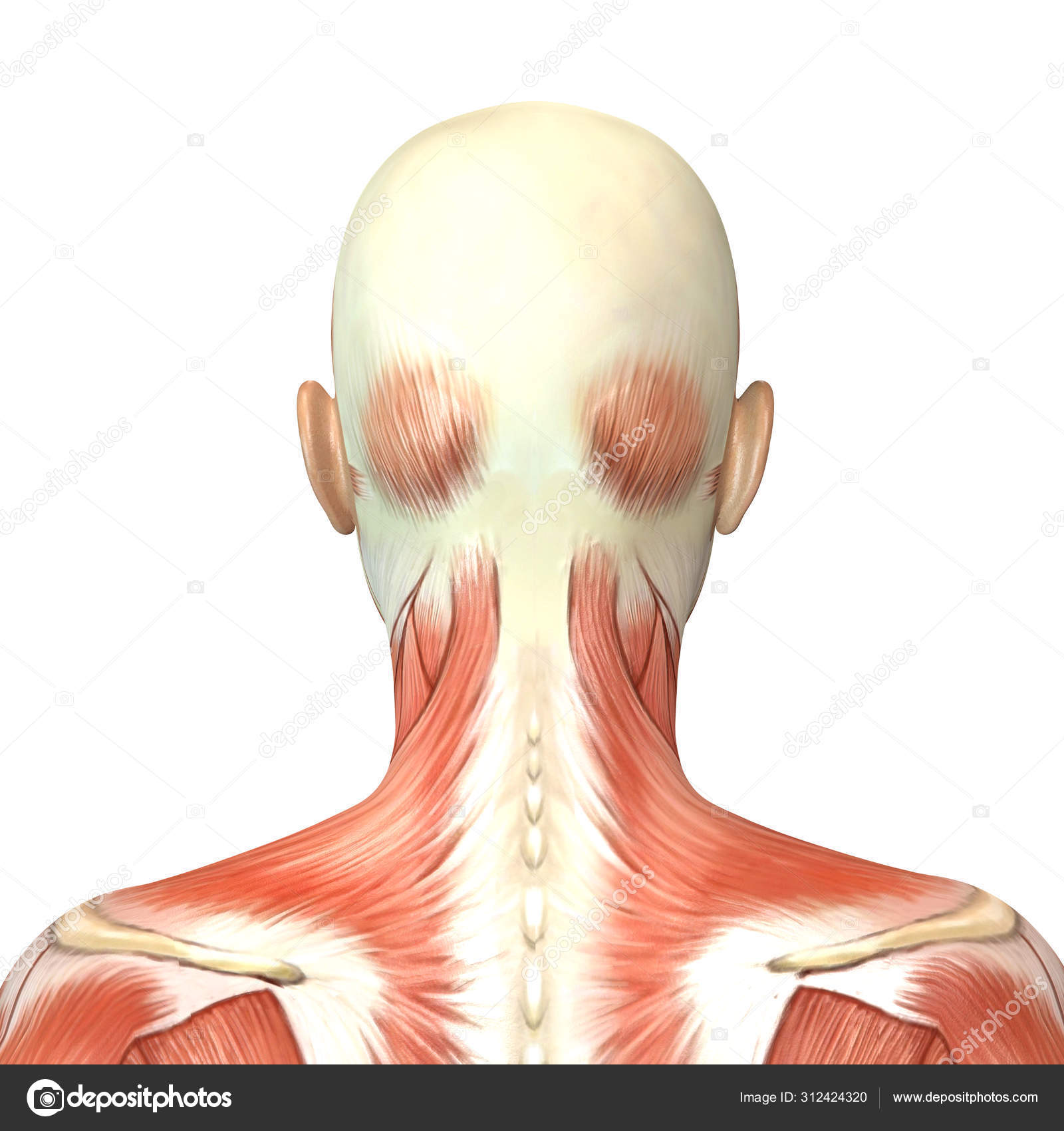



3d Illustration Of Female Head Muscles Anatomy Back View Stock Photo By C Deryadraws
Muscle Back Of Head Anatomy Anatomy Massage Therapy Migraine / Admin Sabtu, 25 September 21 Head impacts increase the risk for concussio We appreciate your review of the support network In general, muscles work when calcium ions are released, which triggers muscle cells to contract Whether they come at night or during the day, crampsThe muscle has a frontal belly and an occipital (near the occipital bone on the posterior part of the skull) belly In other words, there is a muscle on the forehead ( frontalis) and one on the back of the head ( occipitalis ), but there is no muscle across the top of the head
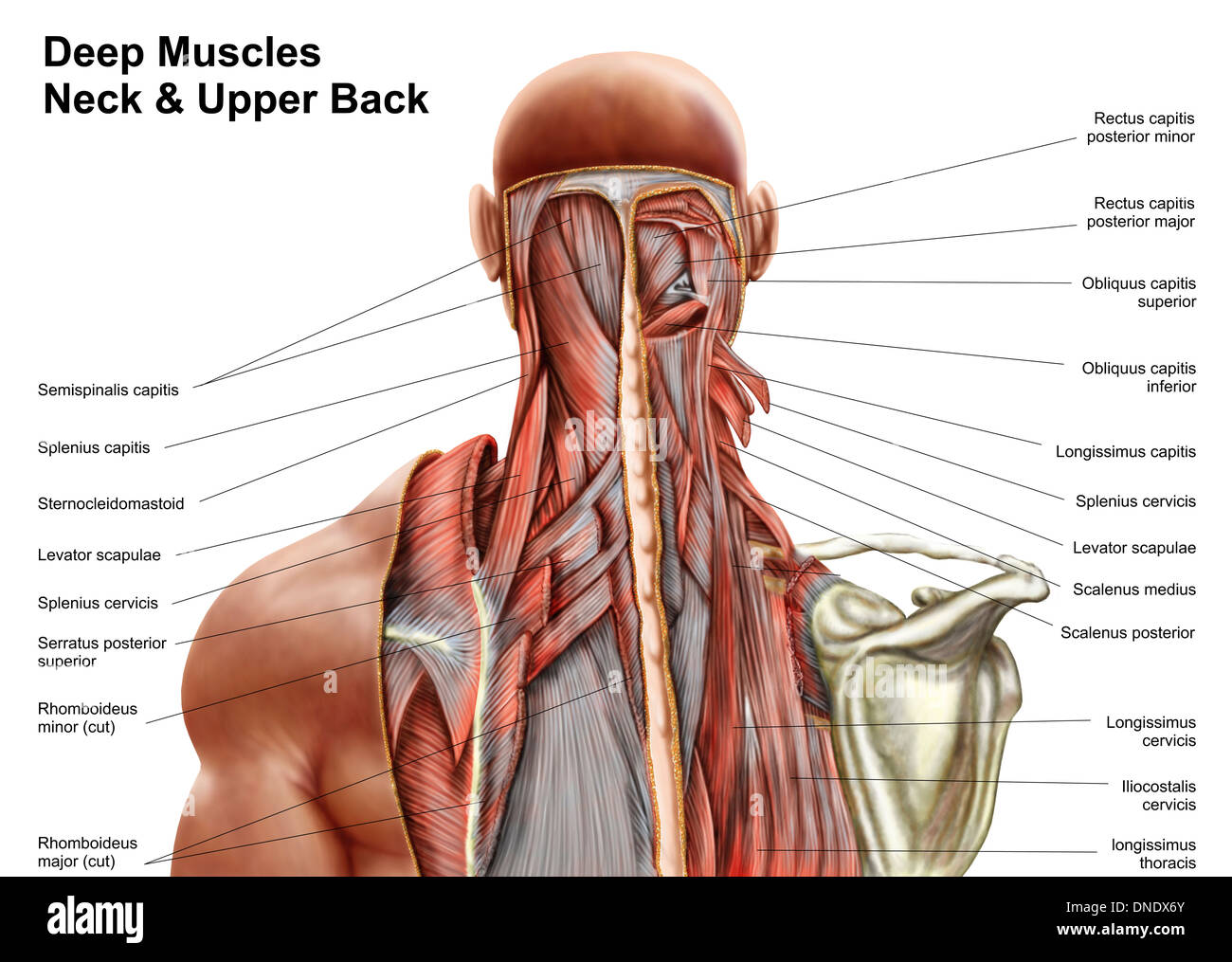



Human Anatomy Showing Deep Muscles In The Neck And Upper Back Stock Photo Alamy
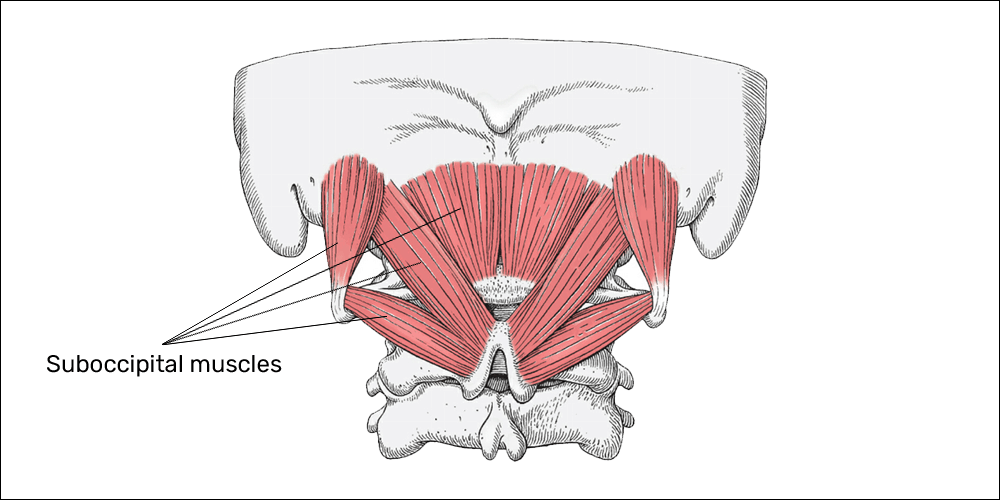



Tension Type Headaches A Common Struggle For Gamers Esports Healthcare



1



Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy Physiology
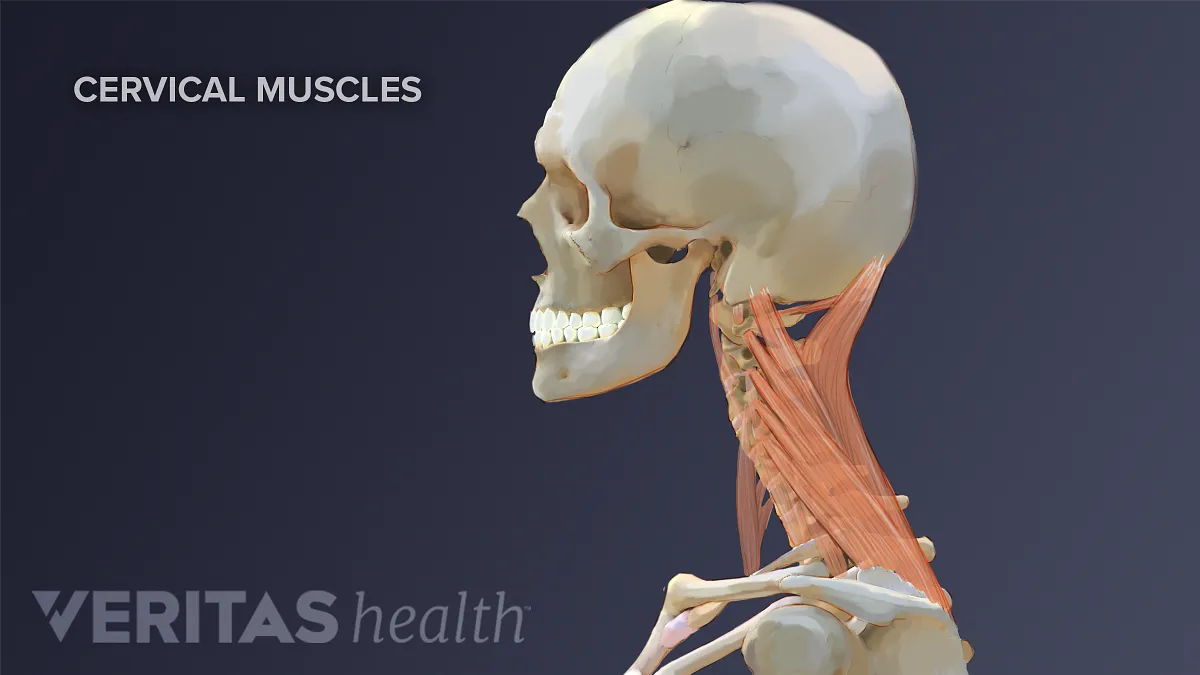



Neck Muscles And Other Soft Tissues



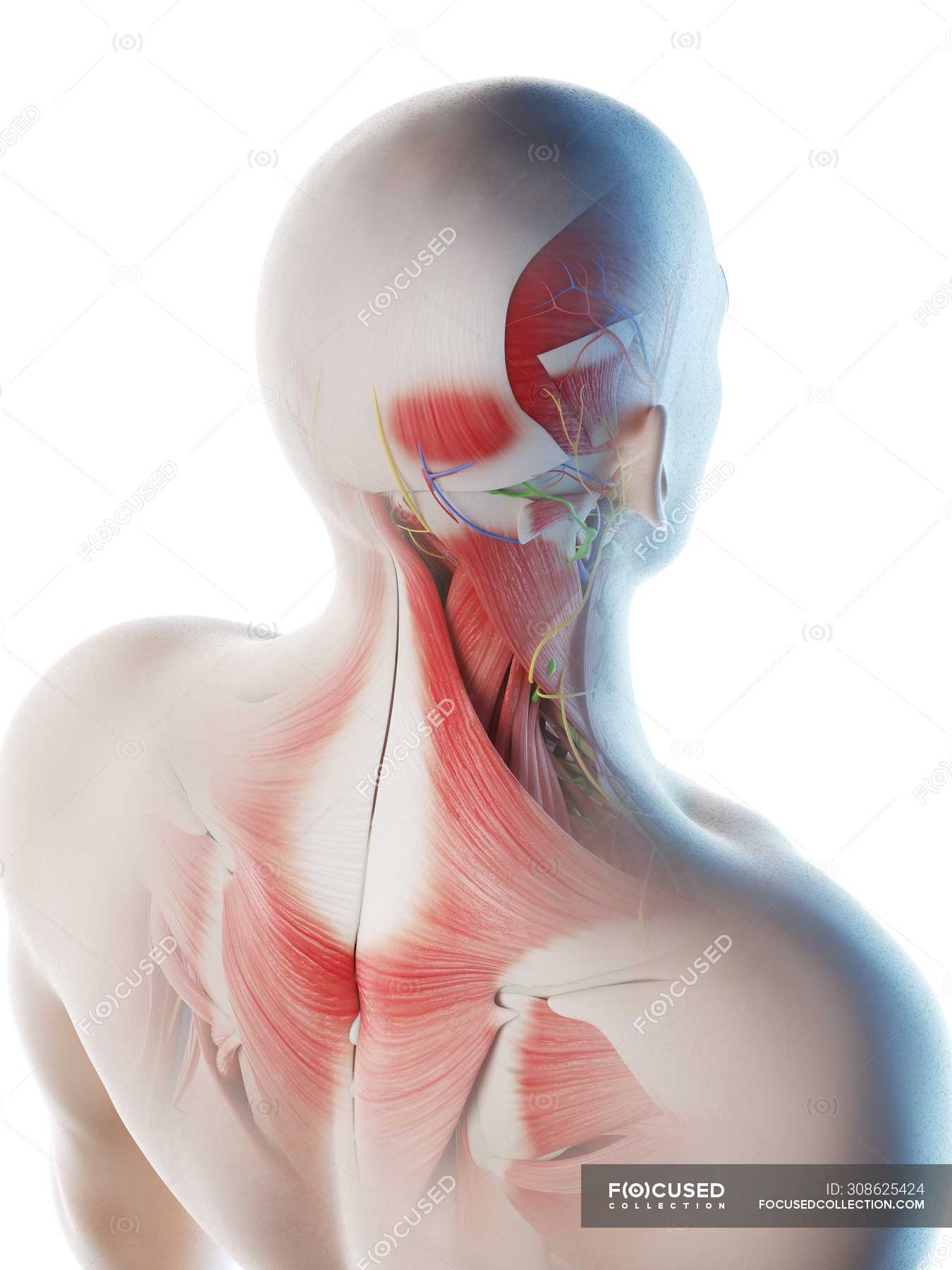
The Anatomy Of Your Tension Headache Somatic Movement Center




Massage For Neck Pain Headaches Suboccipitals




Understanding The Spinotransversales The Superficial Intrinsic Muscles Of The Back



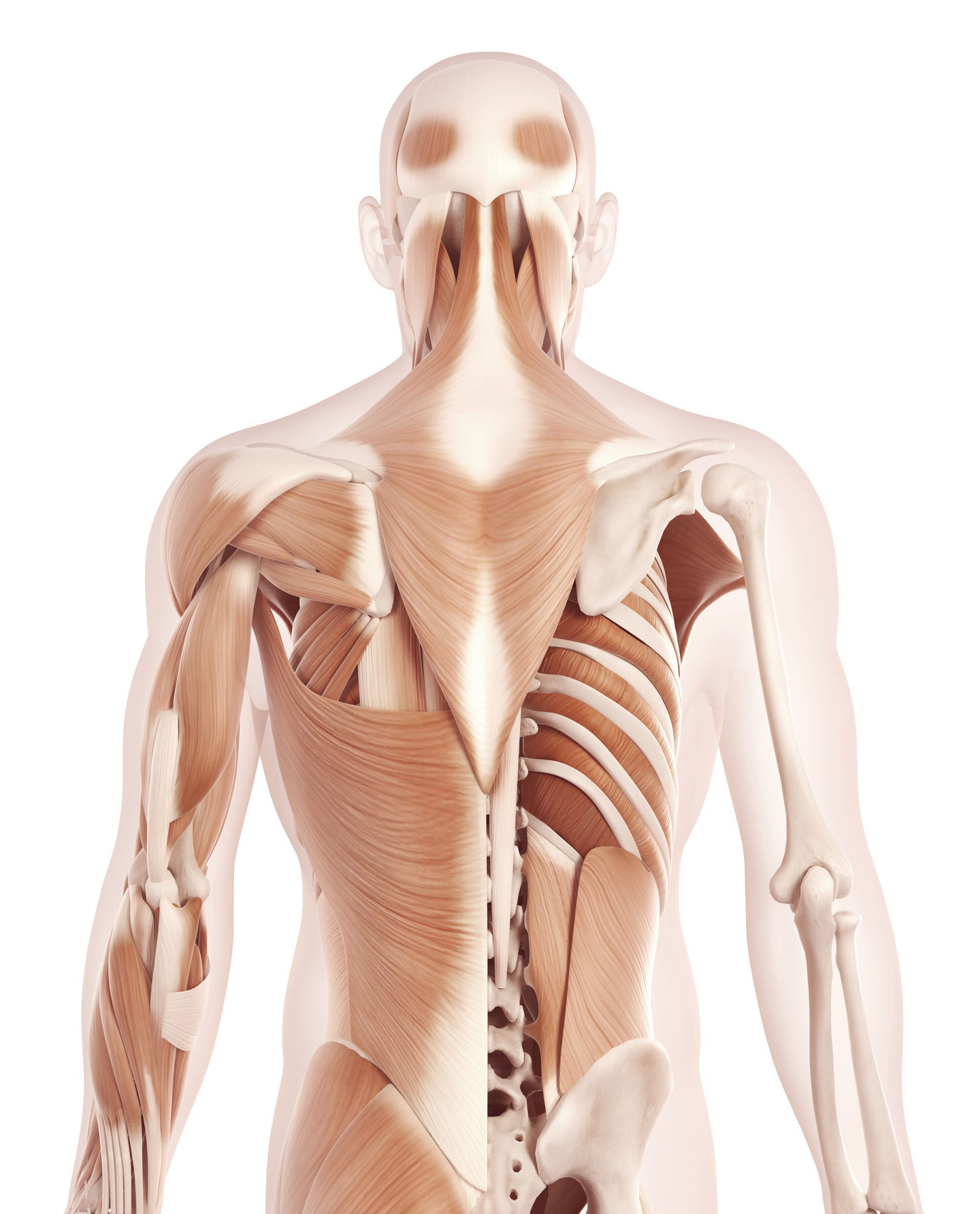
Male Anatomy Of Head Neck And Back With Musculature Computer Illustration Normal Transparent Stock Photo



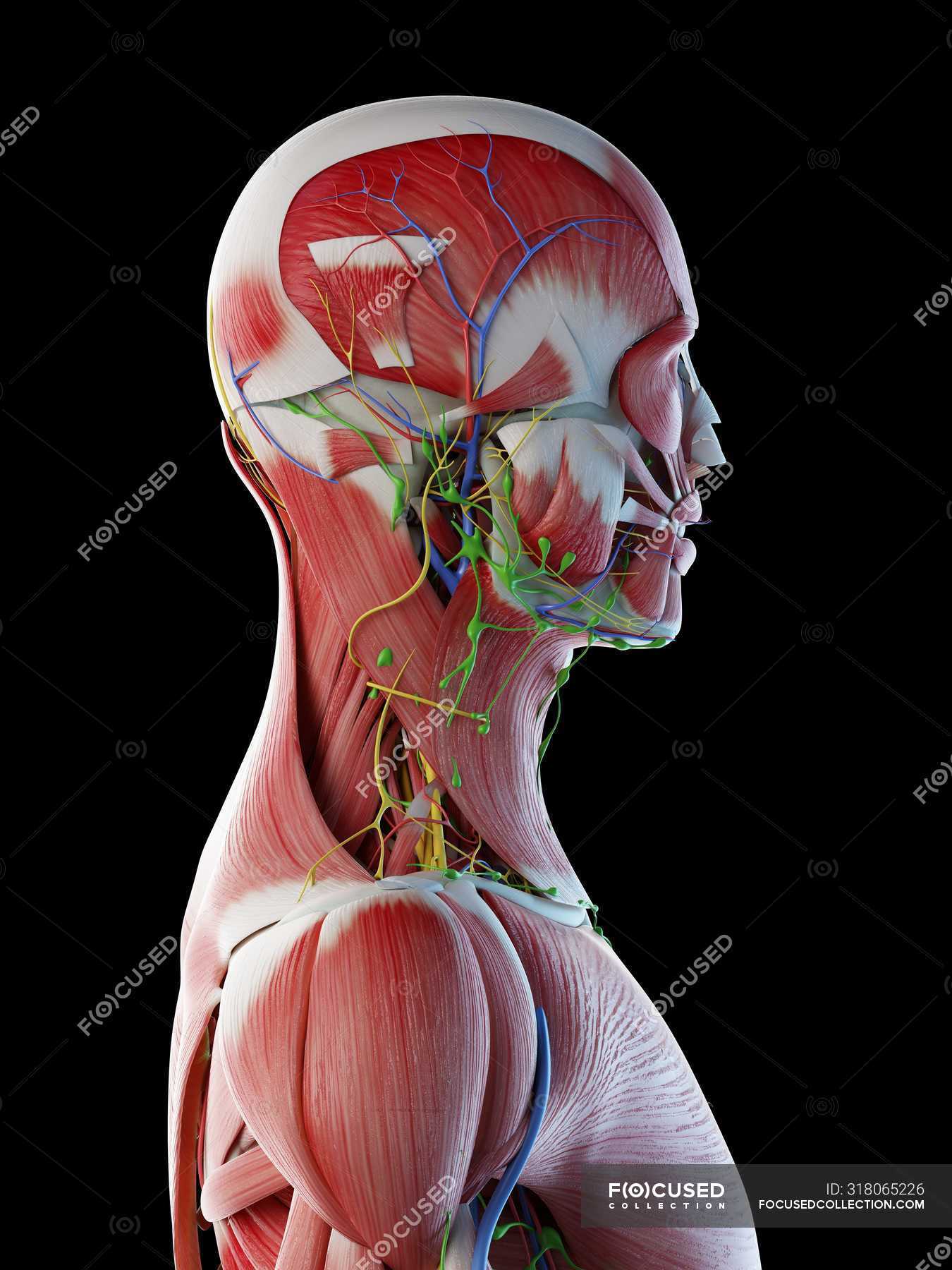
Male Back Neck And Head Muscles Computer Illustration 3d Artwork Stock Photo
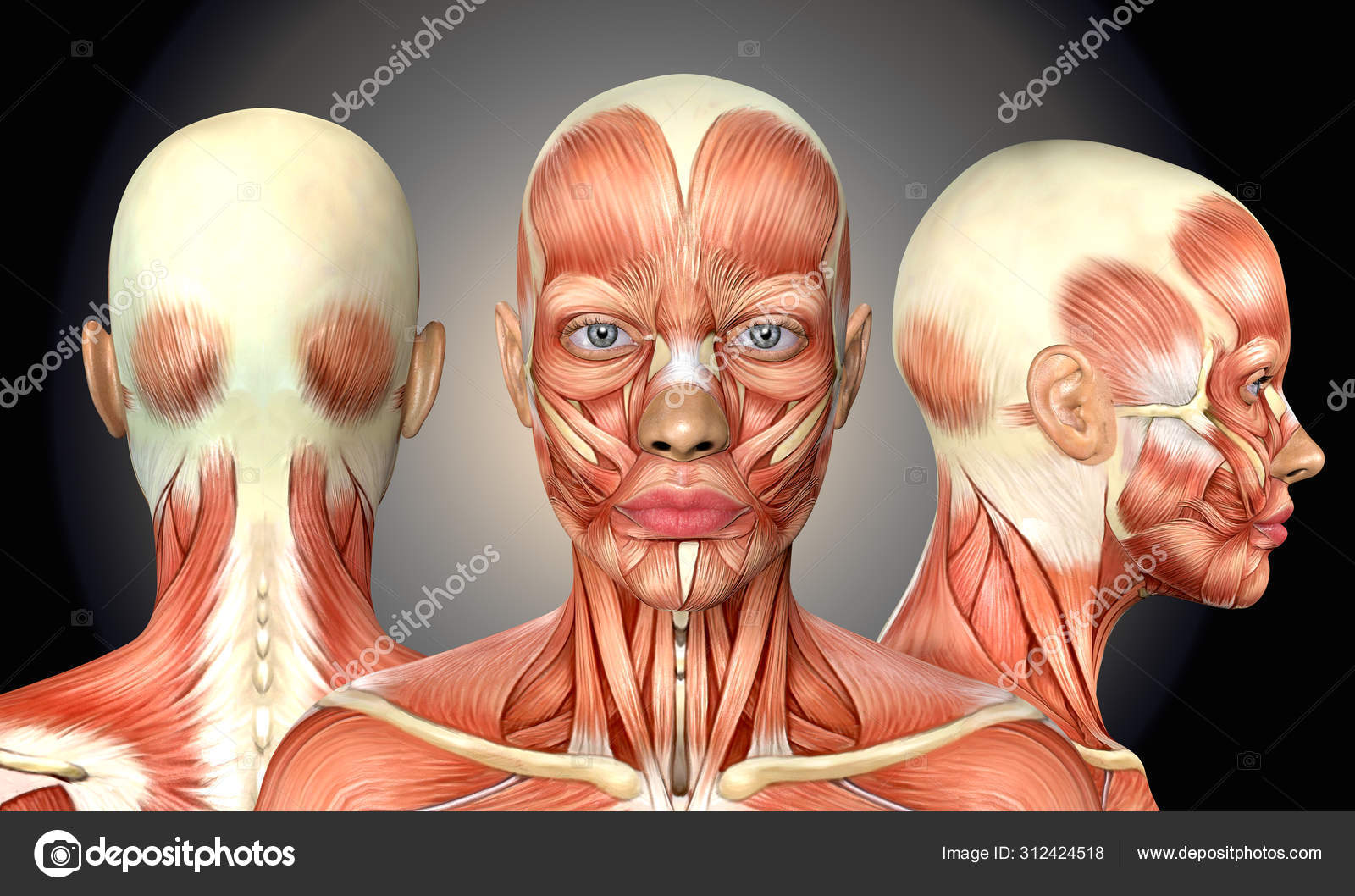



3d Illustration Of Female Head Muscles Anatomy With Front Back A Stock Photo By C Deryadraws
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/10606/Head_Thumbnail__1_.png)



Head Anatomy Muscles Glands Arteries And Nerves Kenhub
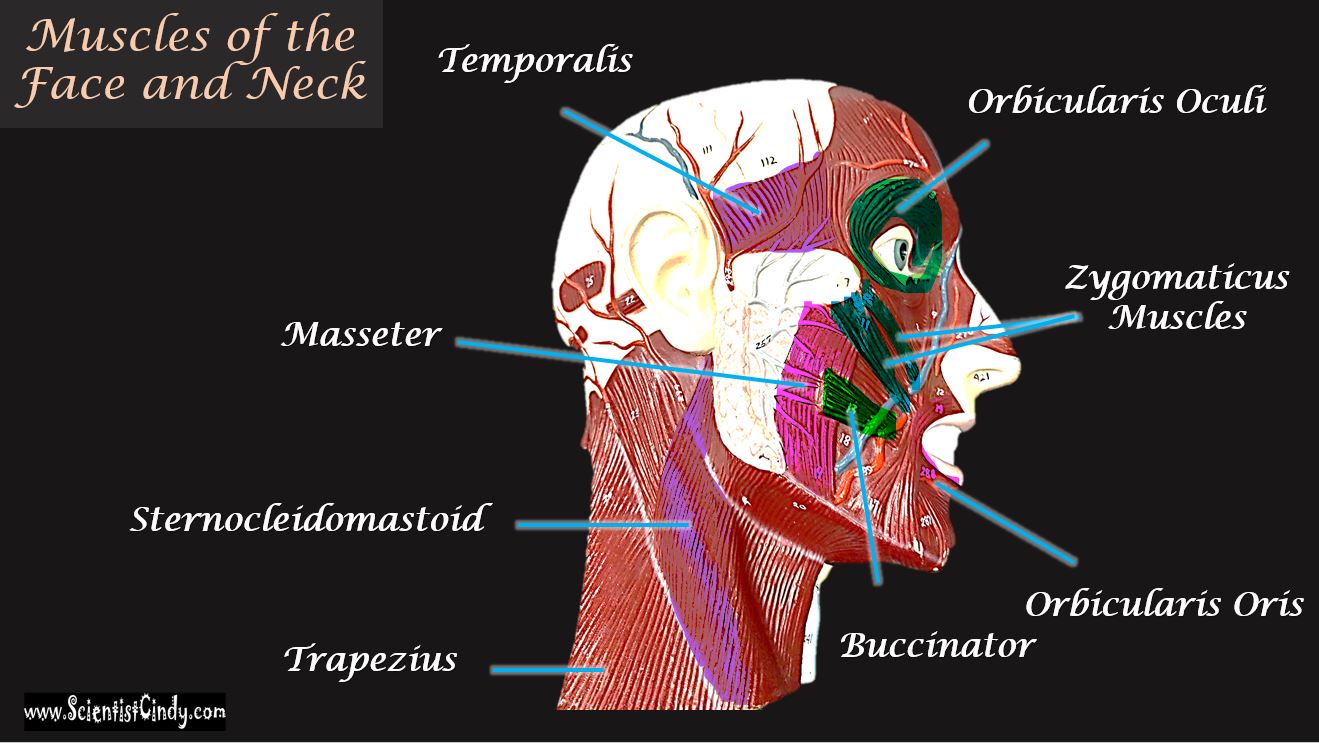



The Muscles Of The Head Trunk And Shoulders Scientist Cindy
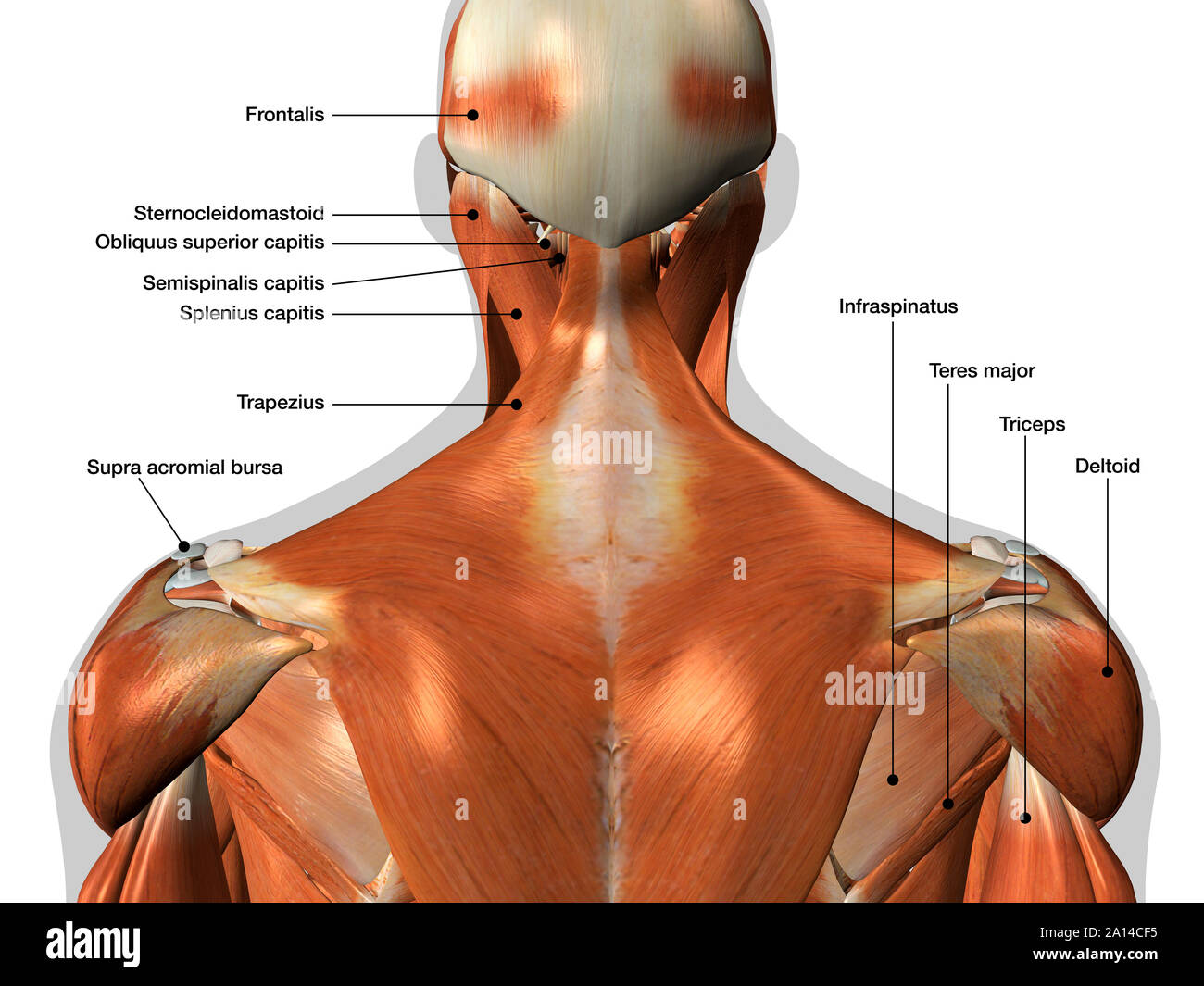



Labeled Anatomy Chart Of Neck And Back Muscles On White Background Stock Photo Alamy




Medical 3d Illustration Of The Upper Back Muscles Canstock




Human Anatomy Showing Face Head Shoulders And Back Muscular Posters For The Wall Posters Medicals Organ Bone Myloview Com
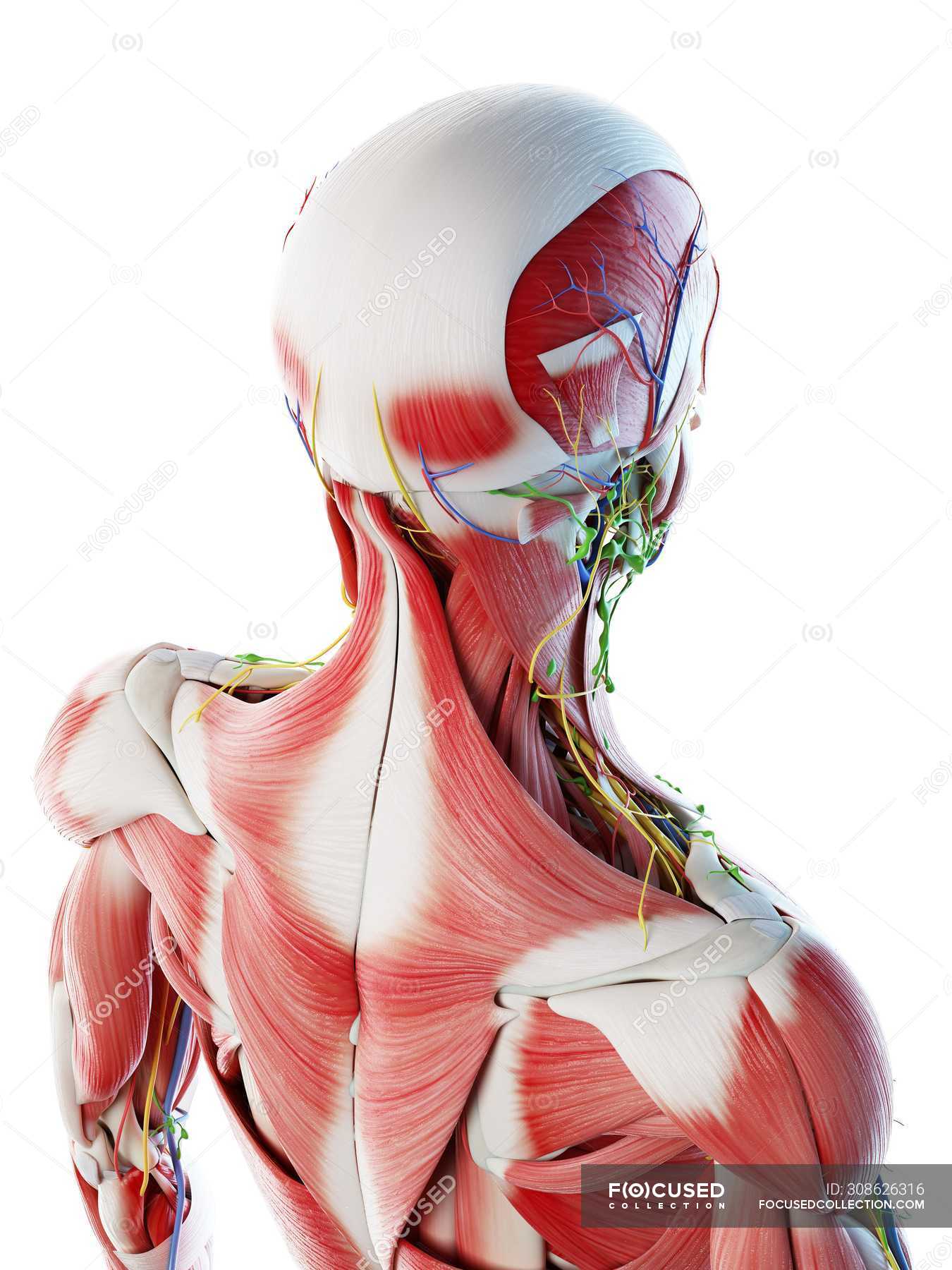



Male Back Neck And Head Muscles Computer Illustration Anatomical 3d Model Stock Photo
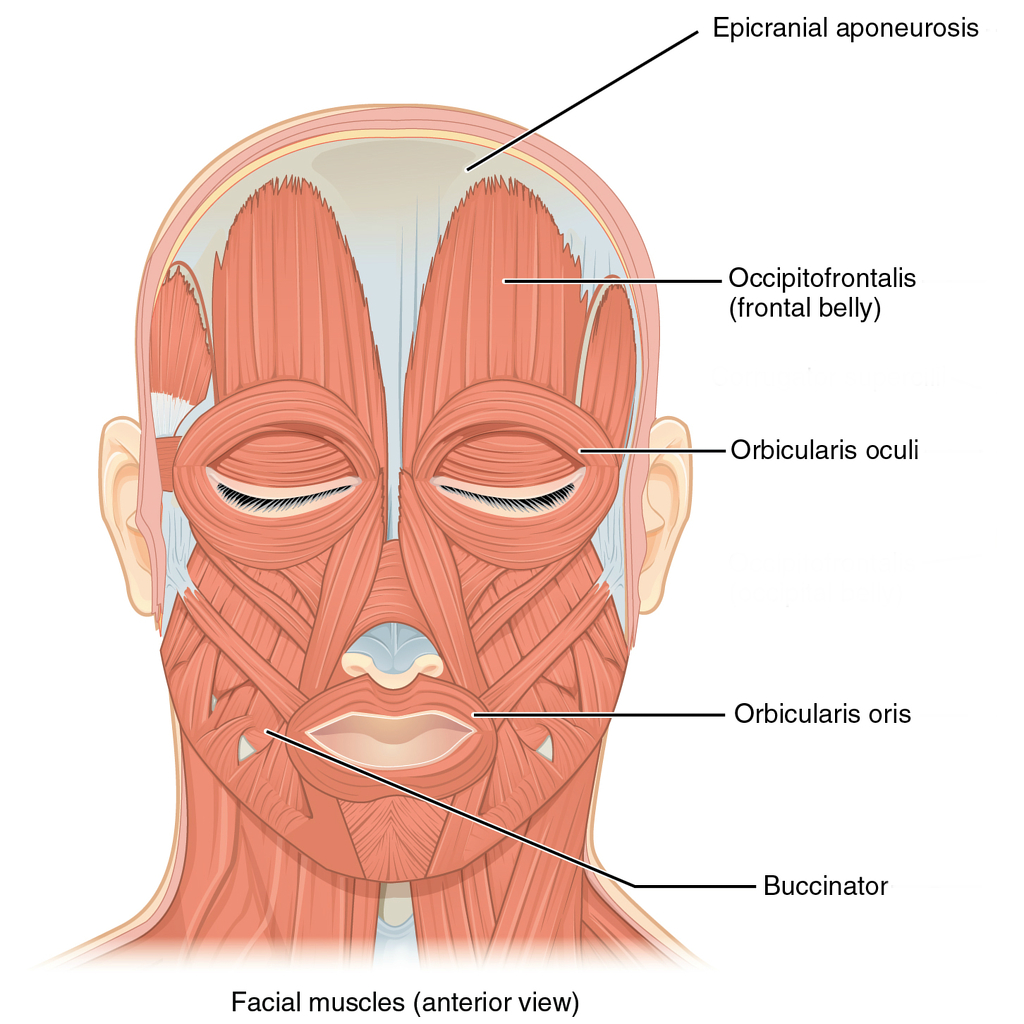



Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Illustrations Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org




Left Muscles Of The Head And Trunk Back View Right Muscles Of The Thigh And Leg Back View Coloured Drawing 18 Wellcome Collection
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/945/wUYoDVvwwuphLXN2qvhA_primary-authochtone-back-muscles_english.jpg)



Back Muscles Anatomy And Functions Kenhub
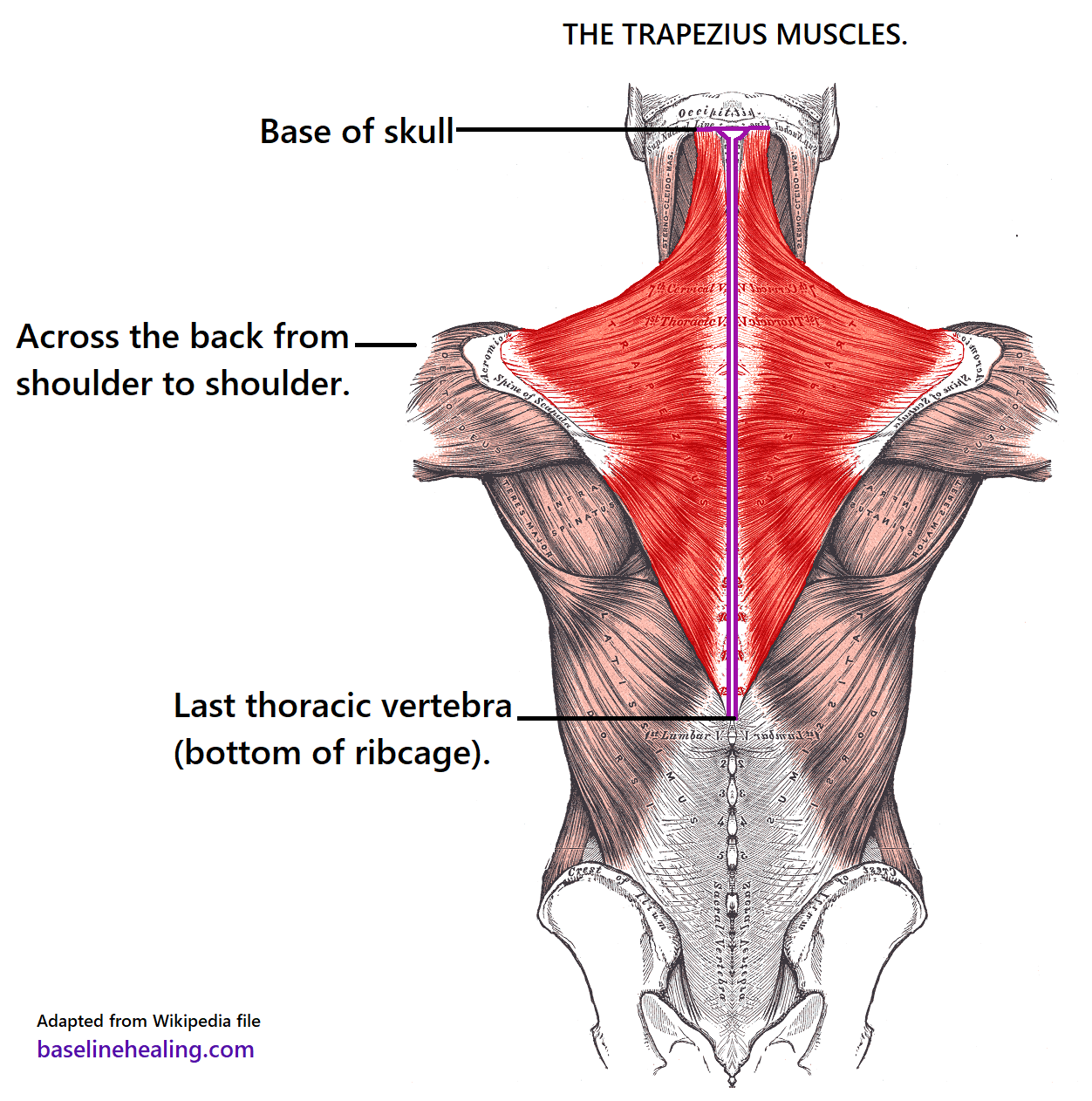



Trapezius Muscles Anatomy Attachments In Detail
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12644/Ventral_trunk_muscles.png)



Muscles Of The Trunk Anatomy Diagram Pictures Kenhub
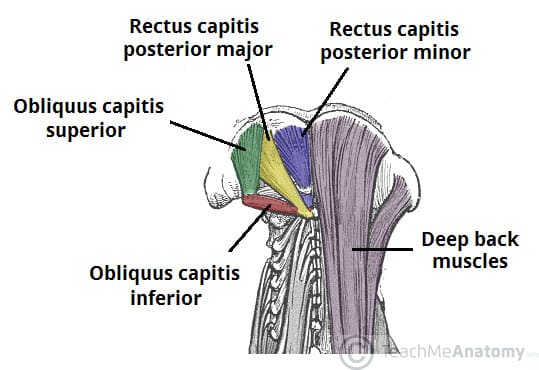



Suboccipital Muscles Attachments Actions Innervation Teachmeanatomy




Labeled Anatomy Chart Of Male Triceps And Back Muscles On White Background Stock Photo Download Image Now Istock
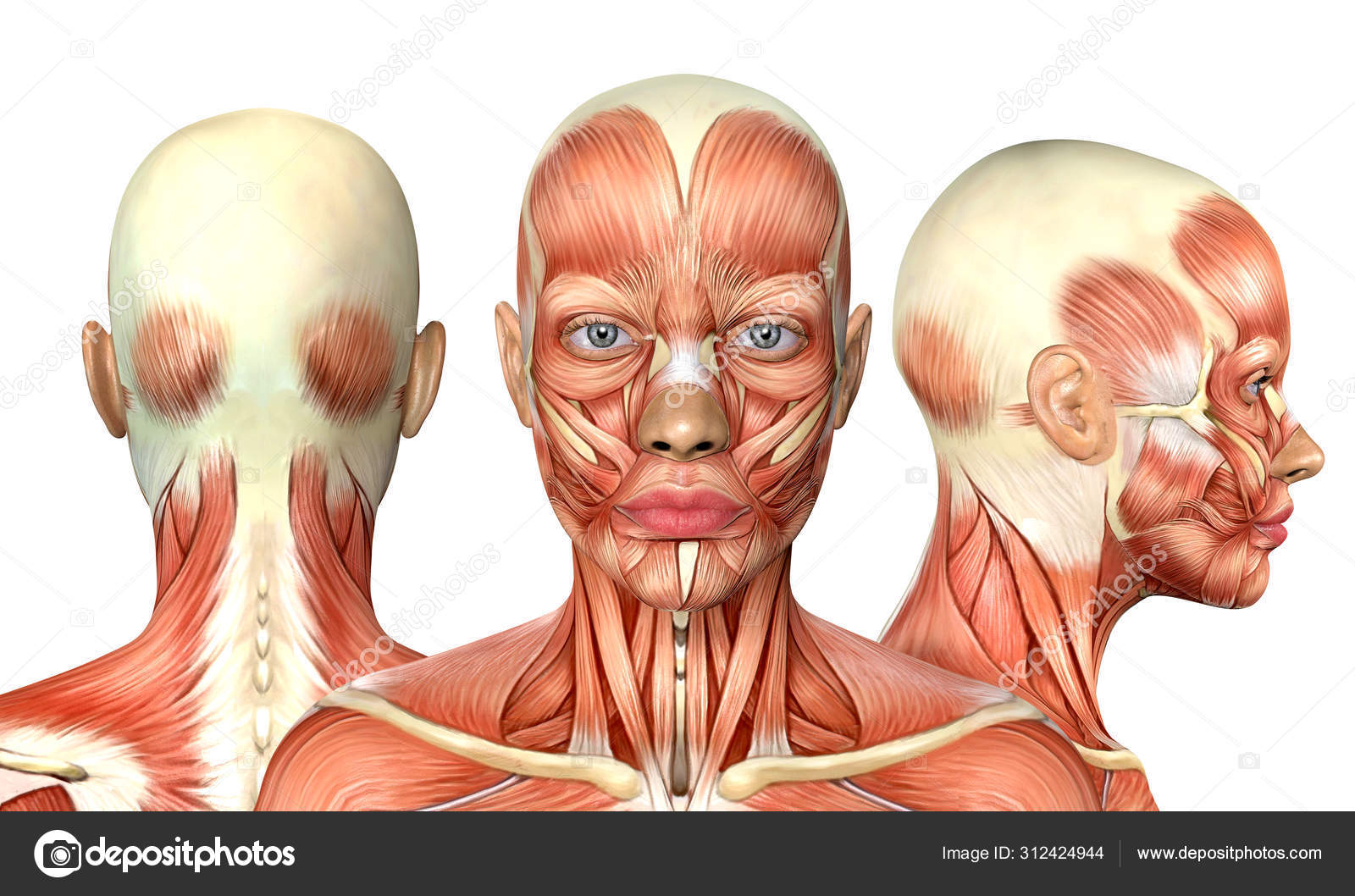



3d Illustration Of Female Head Muscles Anatomy With Front Back A Stock Photo By C Deryadraws




Muscles Of Neck Lateral View Neck Muscle Anatomy Muscle Anatomy Human Anatomy



1




Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And Physiology I
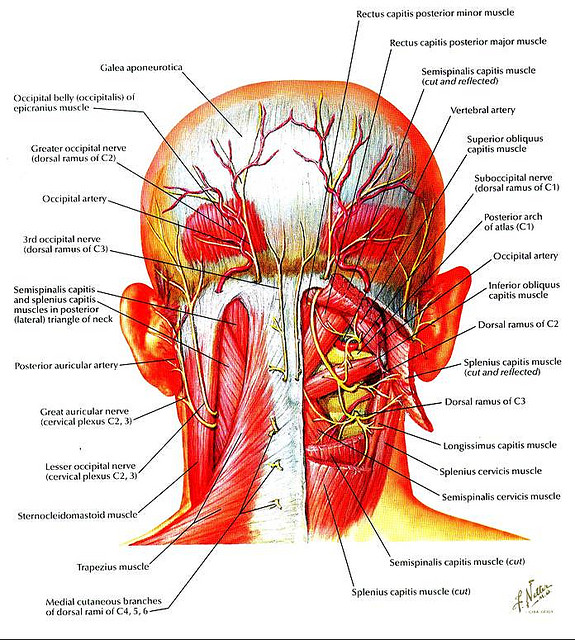



Head And Neck Muscles Diagram Wiring Site Resource
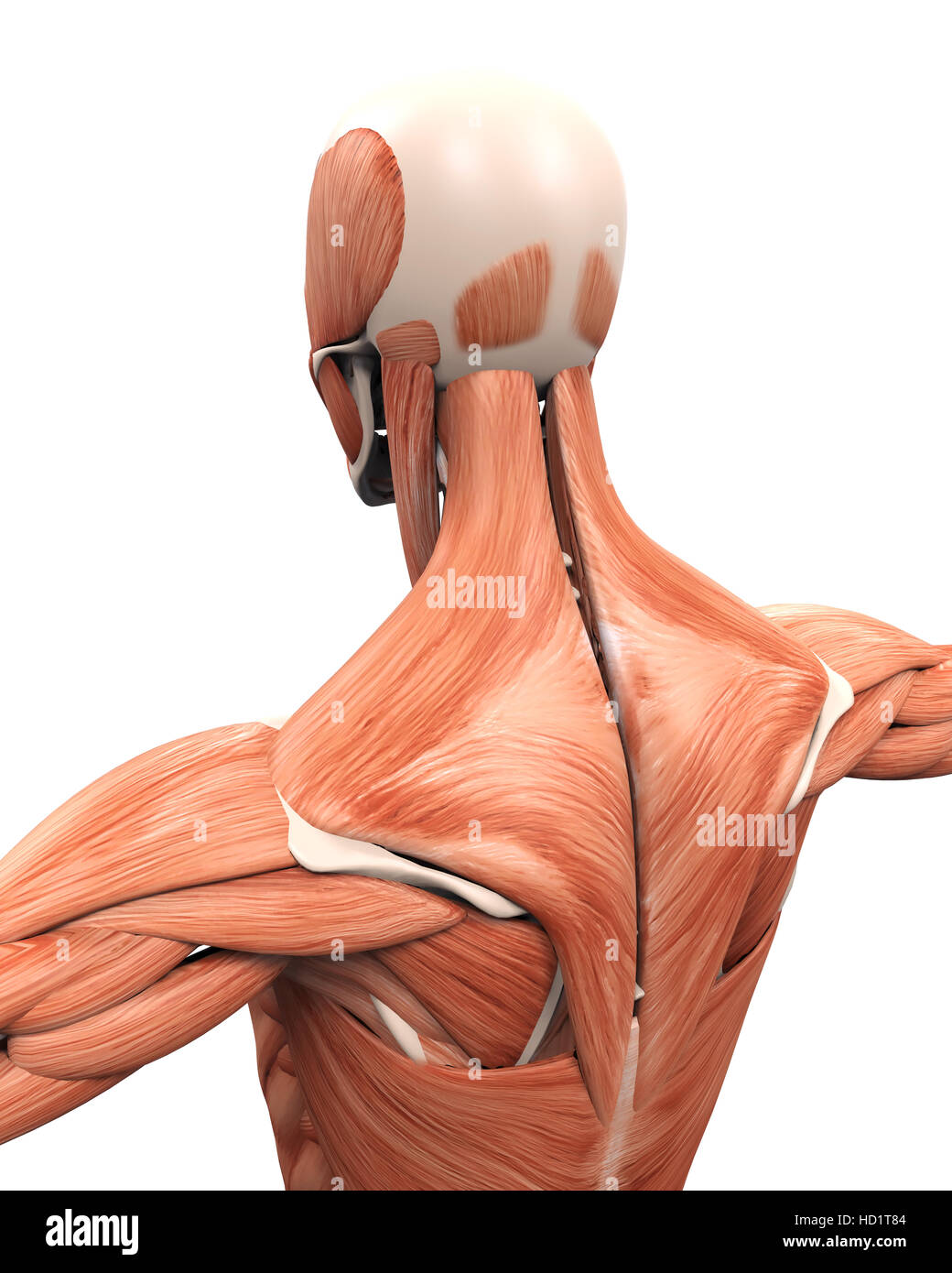



Muscular Anatomy Of The Back Stock Photo Alamy
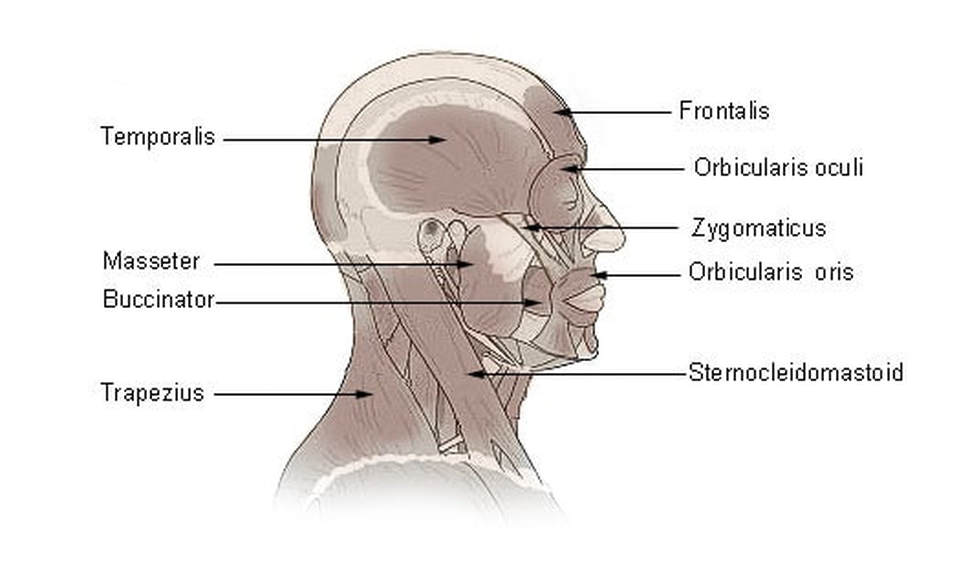



The Muscles Of The Head Trunk And Shoulders Scientist Cindy




Female Head Muscles Anatomy Side View Stock Photo Download Image Now Istock
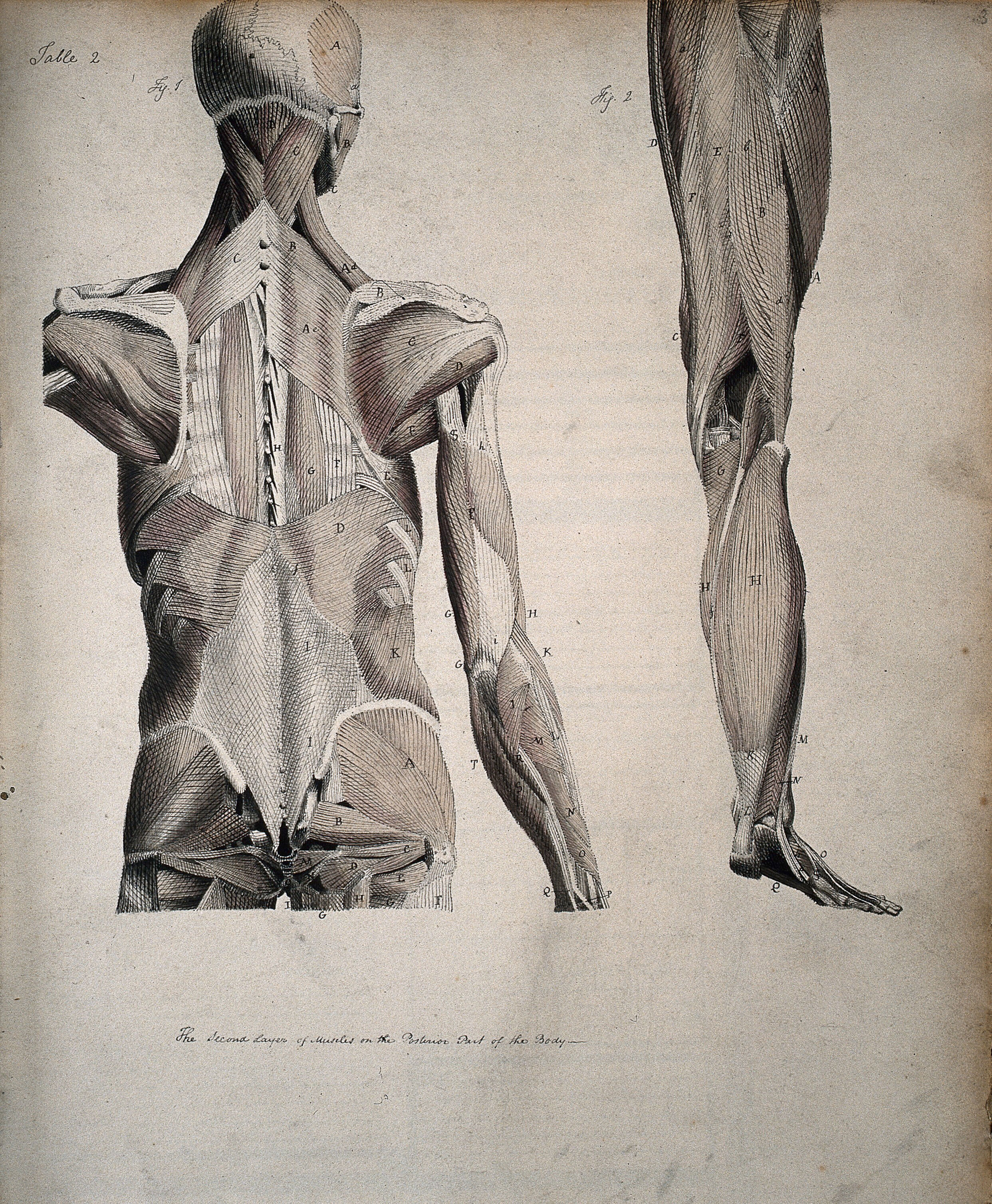



Left Muscles Of The Head And Trunk Back View Right Muscles Of The Thigh And Leg Back View Coloured Drawing 18 Wellcome Collection




Muscles Advanced Anatomy 2nd Ed
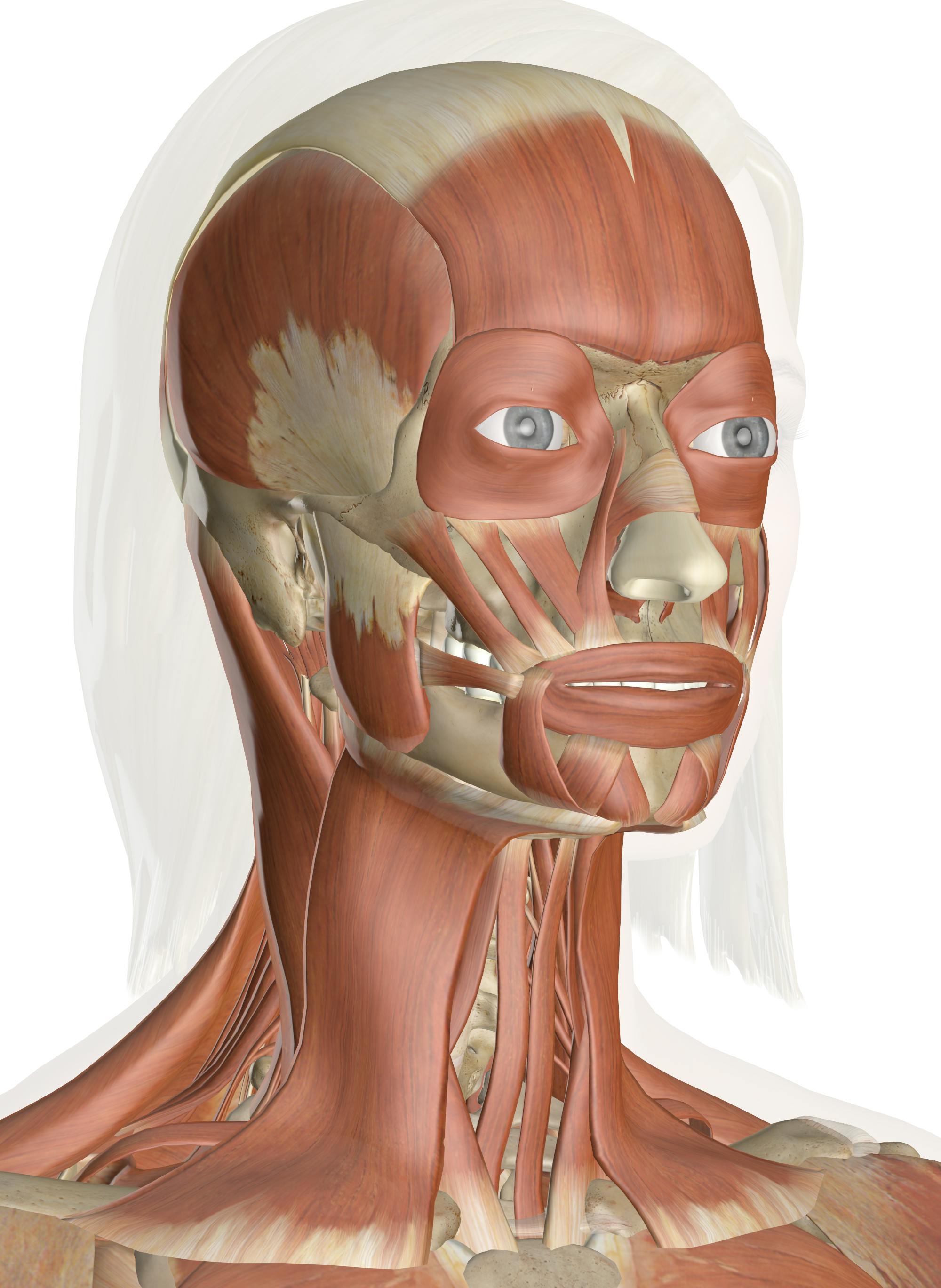



Muscles Of The Head And Neck Anatomy Pictures And Information
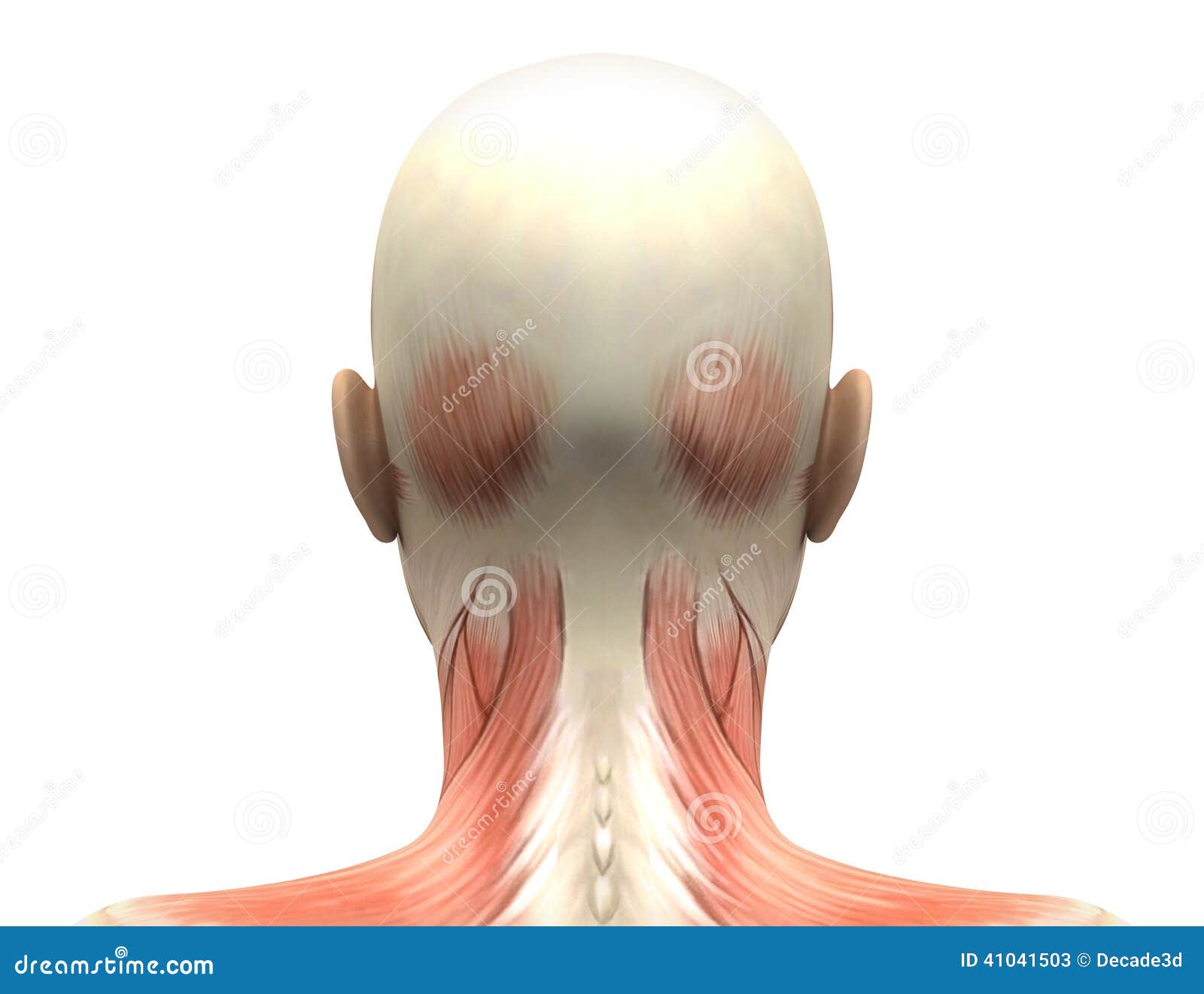



Female Head Muscles Anatomy Back View Stock Illustration Illustration Of Posterior Female
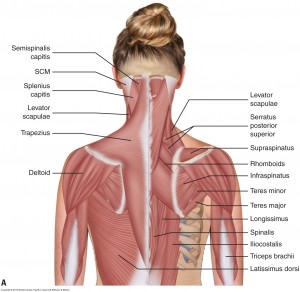



Understanding Chronic Headaches And Fighting The Pain
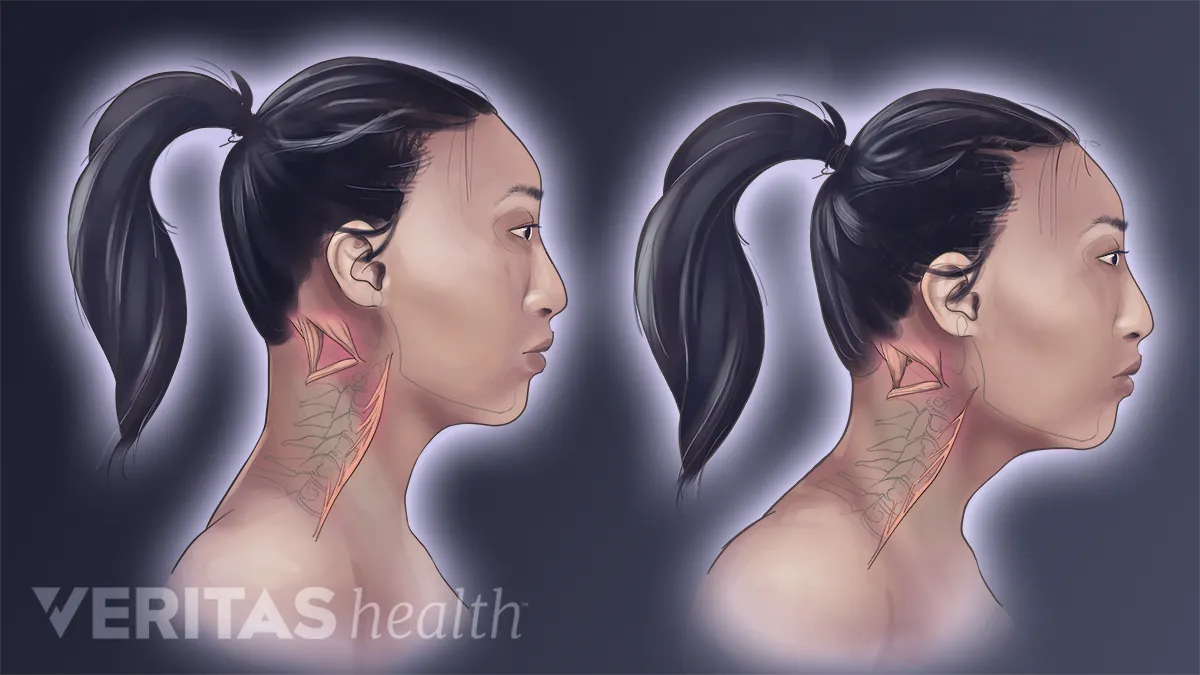



Forward Head Posture S Effect On Neck Muscles



Muscle Anatomy
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/14074/Back_muscles.png)



Back Muscles Anatomy And Functions Kenhub
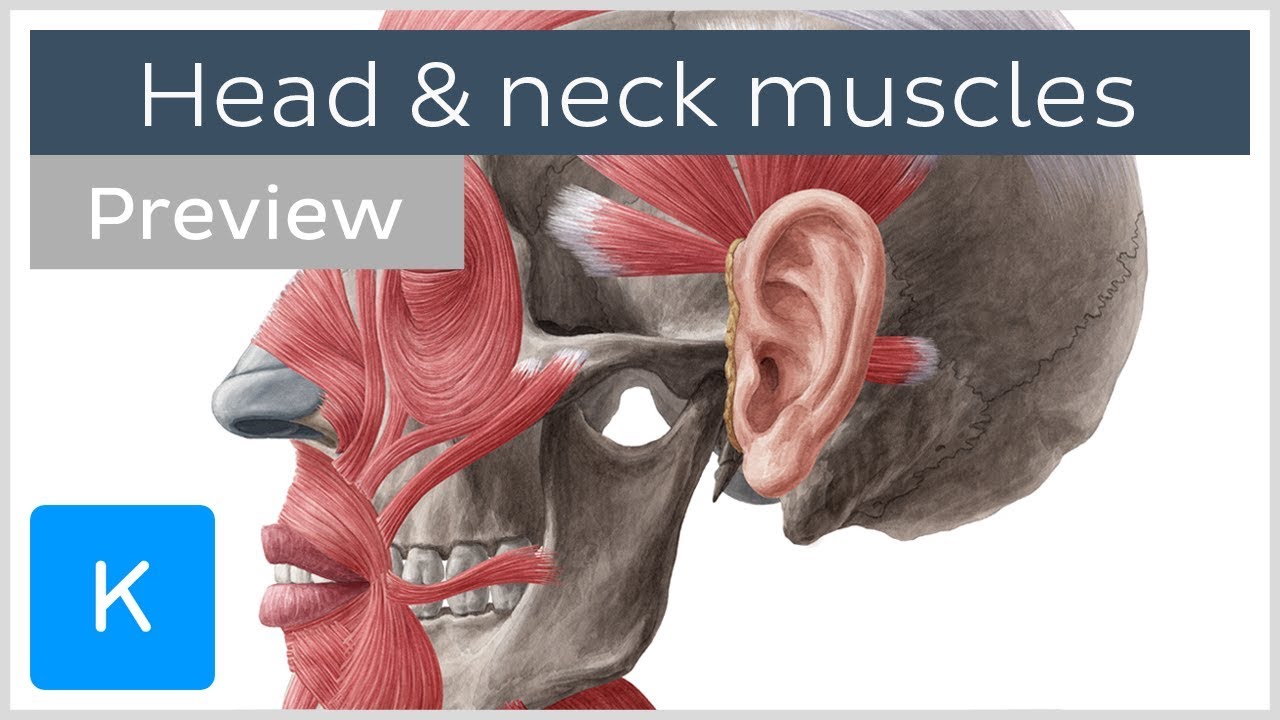



Main Muscles Of The Head And Neck Preview Human Anatomy Kenhub Youtube




Muscle Posterior Triangle Of The Neck Head And Neck Anatomy Human Body Trapezius Png Clipart Abdomen




Aponeurosis Png Images Pngegg
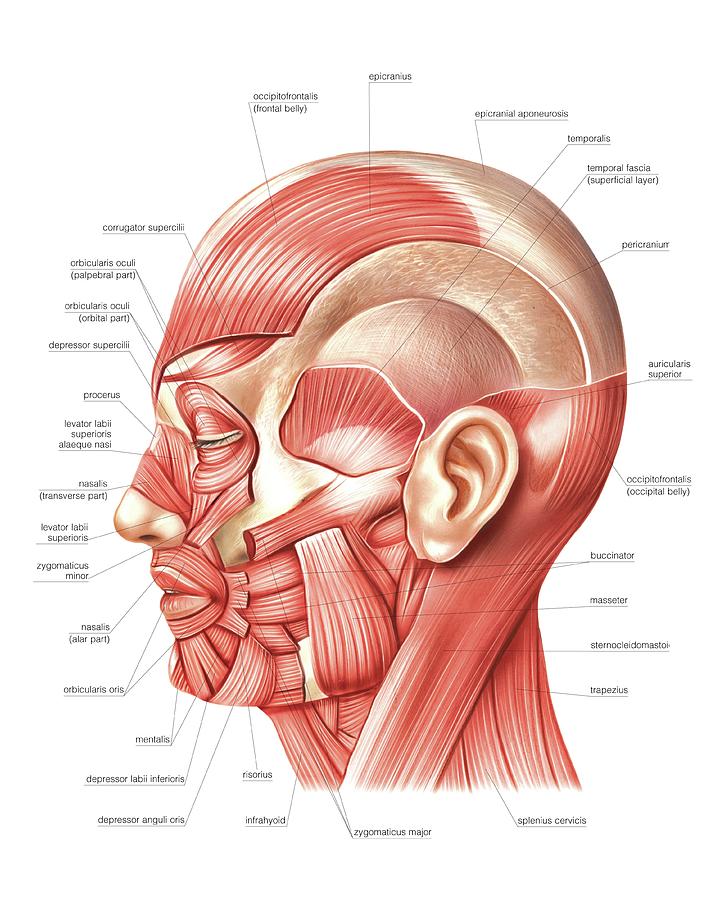



Head Muscles Photograph By Asklepios Medical Atlas
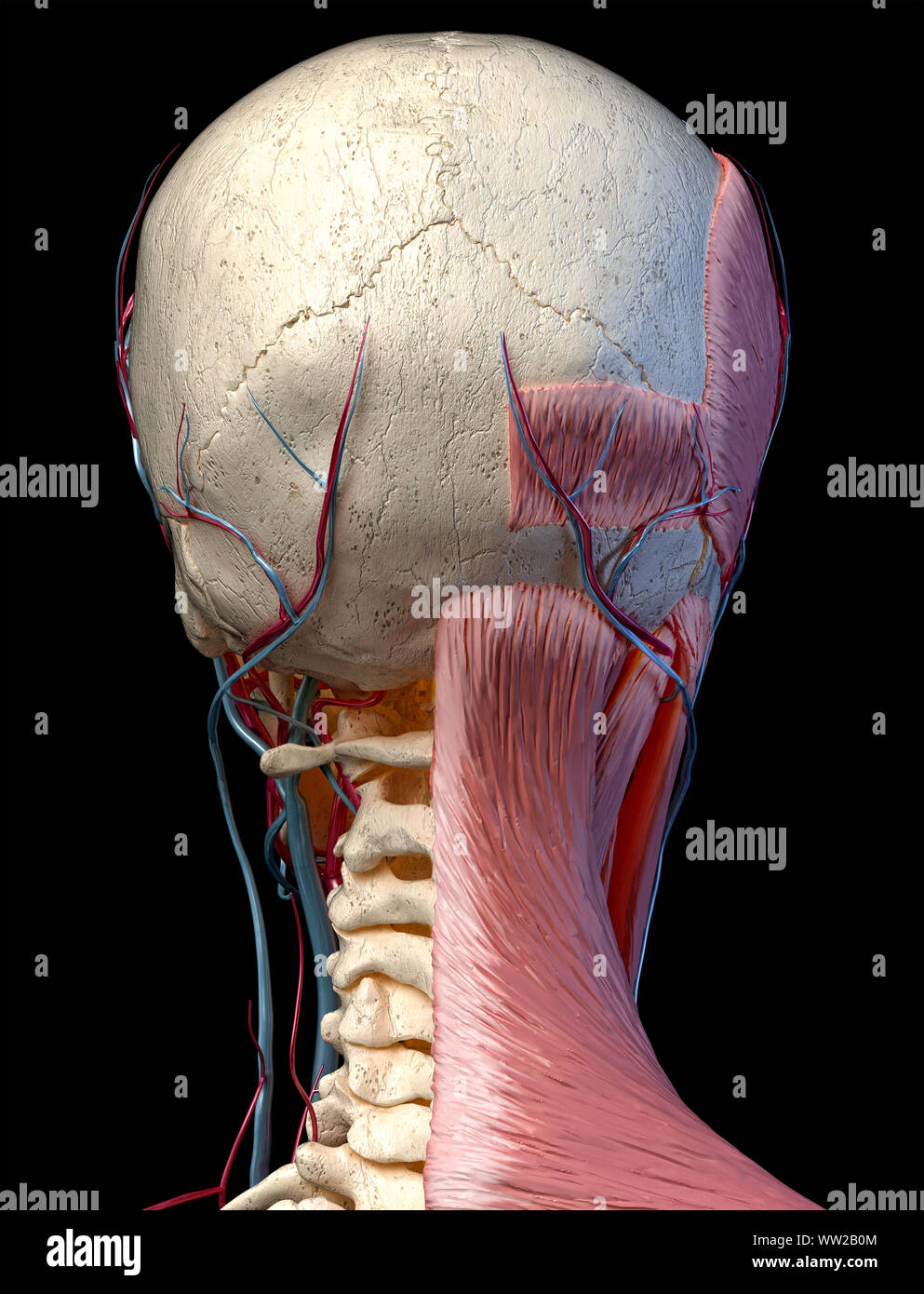



Human Anatomy 3d Illustration Of Head With Skull Blood Vessels And Muscles On Black Background Rear View Stock Photo Alamy
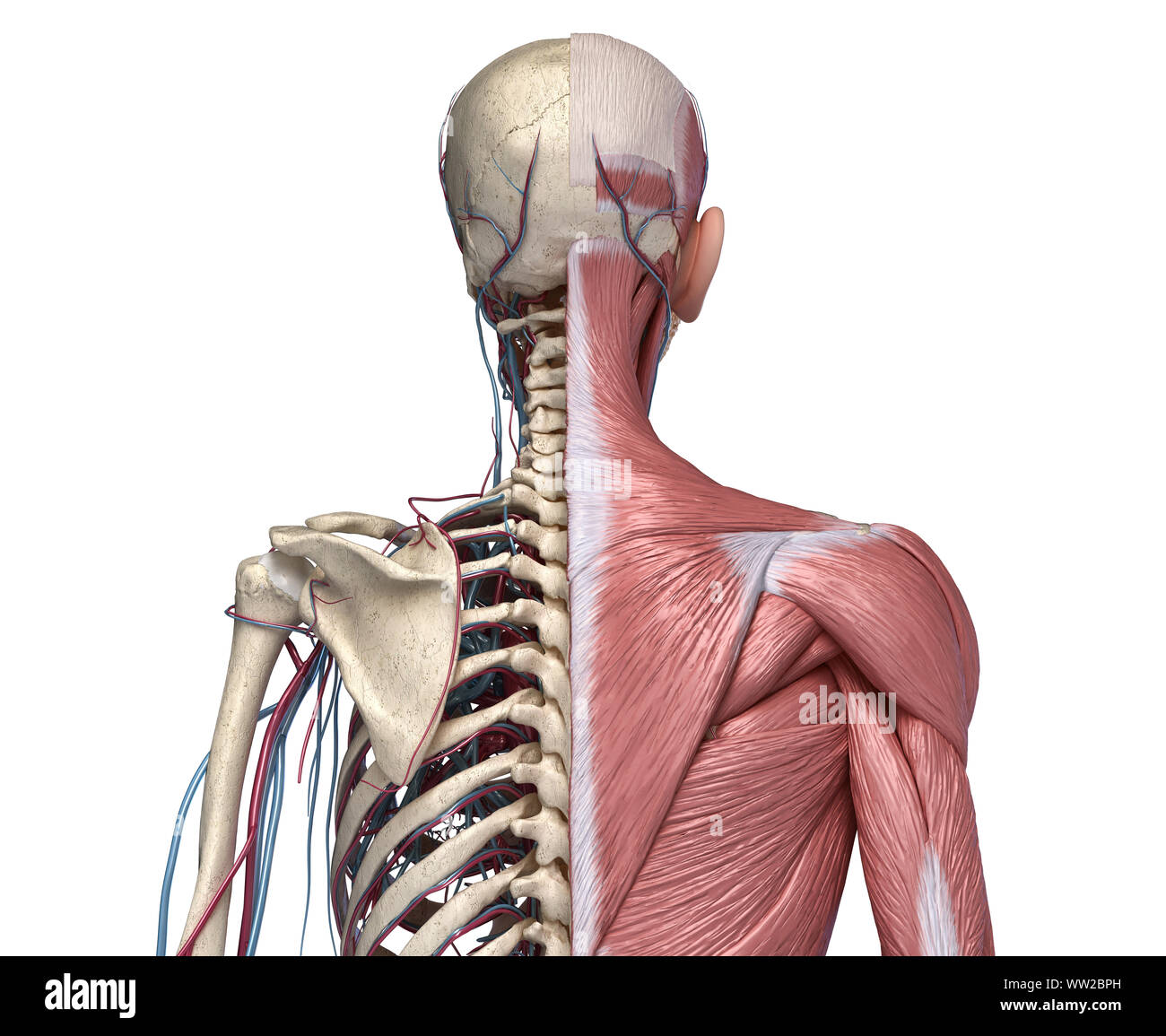



Human Anatomy Torso Skeleton With Muscles Veins And Arteries Back View On White Background 3d Anatomy Illustration Stock Photo Alamy
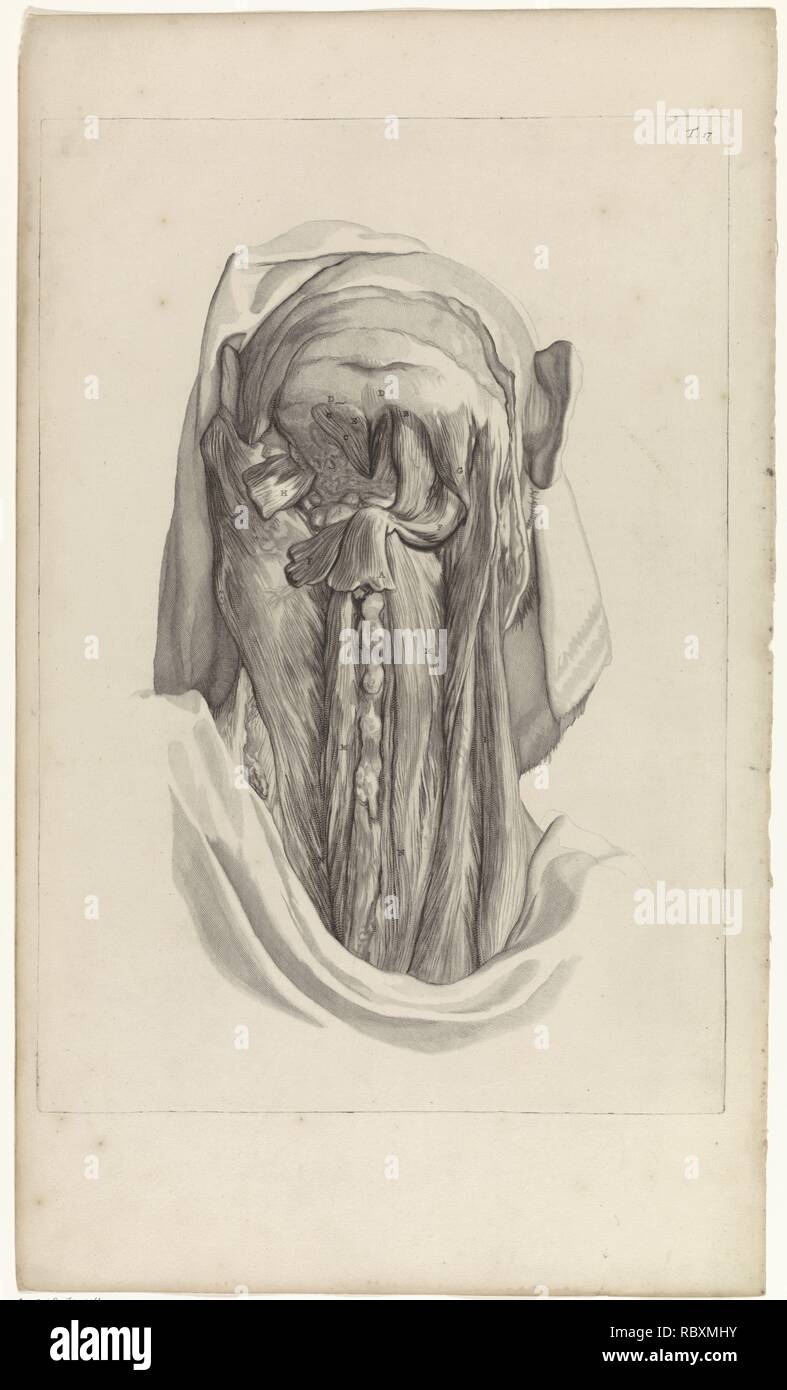



Anatomical Study Of The Muscles Of The Back Of The Head And The Neck Pieter Van Gunst After Gerard De Lairesse 1685 Jpg Rbxmhy Stock Photo Alamy
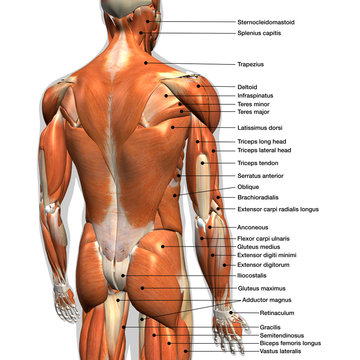



17 470 Best Back Muscles Anatomy Images Stock Photos Vectors Adobe Stock




Jeff Searle Muscles Of The Head And Neck




Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And Physiology I



1



Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And Physiology I




Human Male Body Anatomy Illustration Of A Human Back With Visible Muscles Stock Illustration Illustration Of Black Body




Human Male Body Anatomy Illustration Of A Human Back With Visible Muscles Stock Illustration Illustration Of Black Body




Human Torso Skeleton With Muscles Veins And Arteries Back View Human Anatomy Torso Skeleton With Muscles Veins And Canstock



Muscle Anatomy



The Intrinsic Back Muscles Attachments Actions Teachmeanatomy




Head Muscles Neck Muscle Anatomy Muscle Diagram




Anatomy Of Back Of Head Anatomy Drawing Diagram




Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And Physiology I



Upper Back Pain Anatomy Of The Back The Pain Center Pain Management Care
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/zygomatic-branches-of-facial-nerve/PgQWv0kzu8ANAIxtmdjWg_Rr._zygomatici_nervi_facialis_02.png)



Superficial Nerves Of The Face And Scalp Anatomy Kenhub




Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And Physiology I




Occipital Neuralgia And Suboccipital Headache C2 Neuralgia Treatments Without Nerve Block Or Surgery Caring Medical Florida




Human Back Human Head Human Body Muscle Others Head Human Anatomy Png Pngwing




Muscles Of The Head Neck Anatomy Model Youtube




Occipital Neuralgia And Suboccipital Headache C2 Neuralgia Treatments Without Nerve Block Or Surgery Caring Medical Florida




Facial Muscles And Expressions Classic Human Anatomy In Motion The Artist S Guide To The Dynamics Of Figure Drawing




Medical 3d Illustration Of The Head Muscles Canstock



The Link Between Posture And Chronic Neck And Upper Back Pain Back Pain And Headache Specialist Burke Va Nova Headache Chiropractic Center
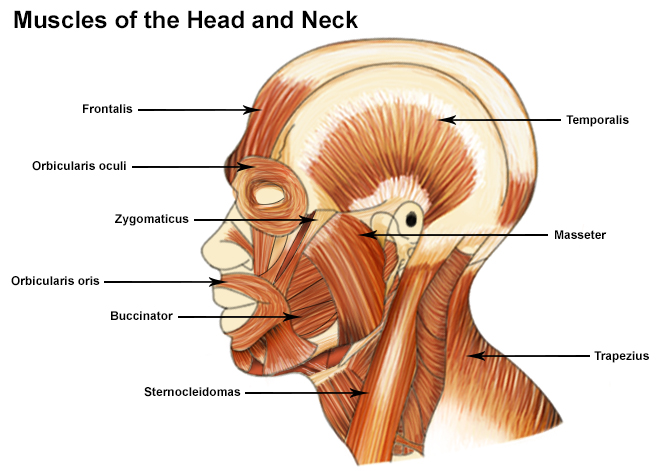



Seer Training Muscles Of The Head And Neck
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-499158129-56a05f075f9b58eba4b0267f.jpg)



Levator Scapula Muscle And Its Role In Pain And Posture




Human Anatomy Neurology Head Shoulder Back Stock Illustration
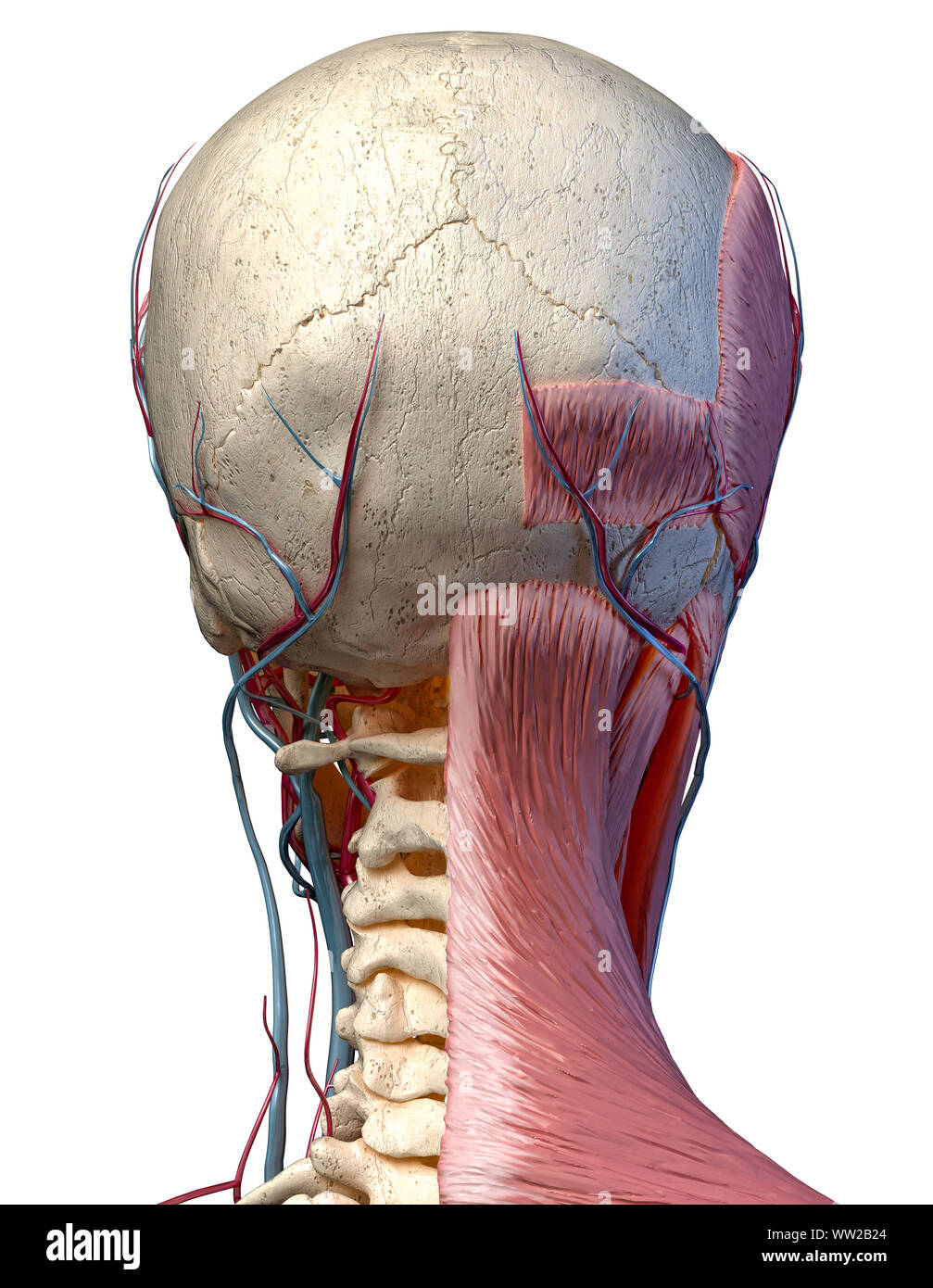



Human Anatomy 3d Illustration Of Head With Skull Blood Vessels And Muscles On White Background Rear View Stock Photo Alamy
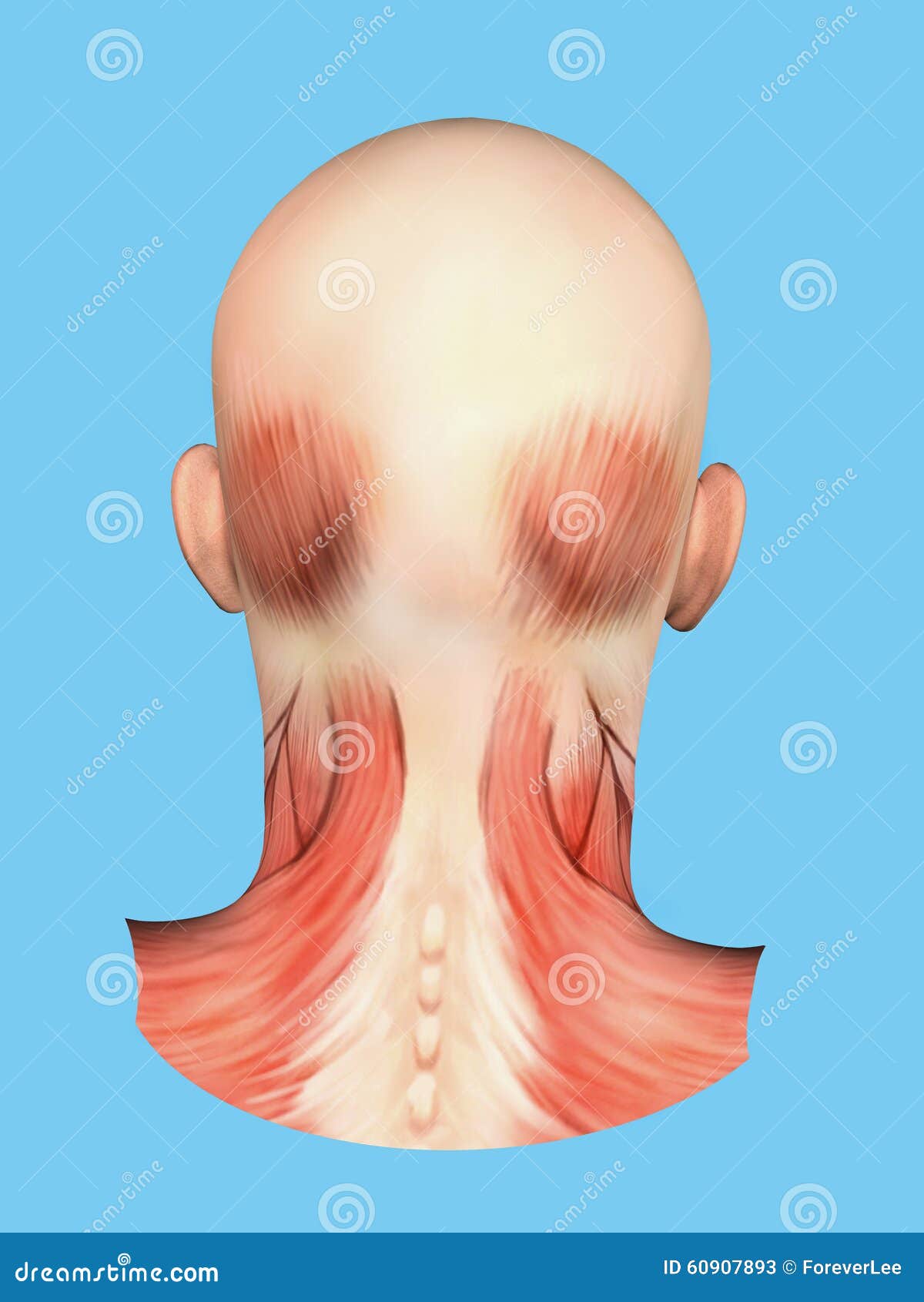



Anatomy Of Muscles On Back Of Head Stock Illustration Illustration Of Sternocleidomastoid Anatomy
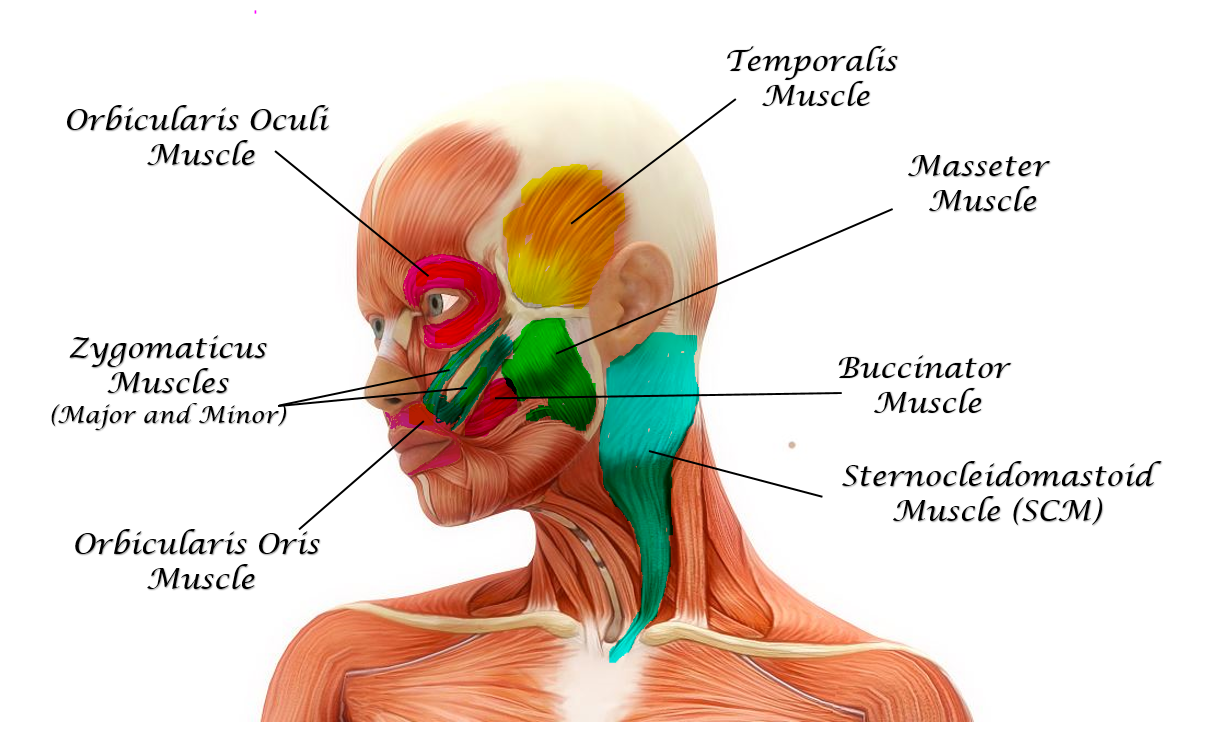



The Muscles Of The Head Trunk And Shoulders Scientist Cindy




Anatomy Drawing Conor Power Neck Muscle Anatomy Muscles Of The Neck Muscle Anatomy
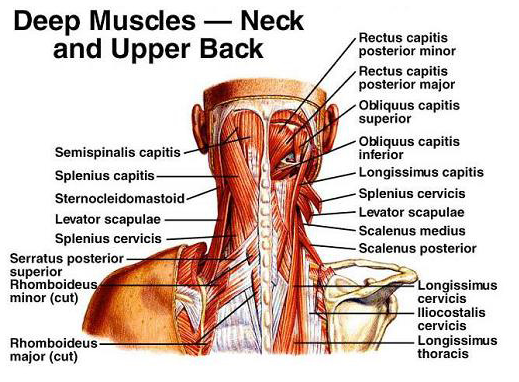



Cervical Motor Control Part 1 Clinical Anatomy Of Cervical Spine Rayner Smale
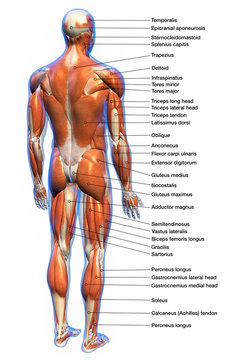



17 470 Best Back Muscles Anatomy Images Stock Photos Vectors Adobe Stock
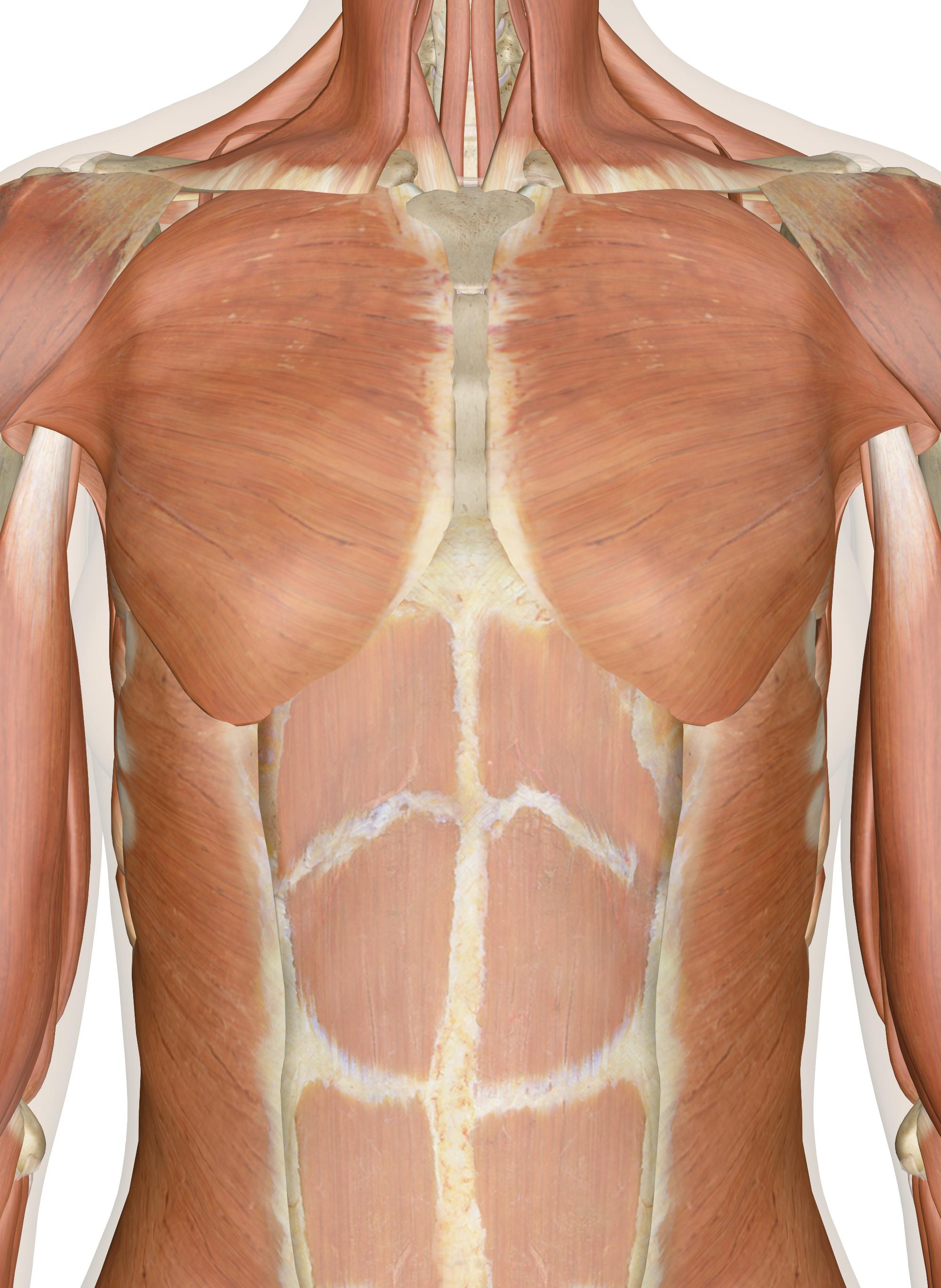



Muscles Of The Chest And Upper Back




Muscle Of The Head And Neck Illustration Stock Image C039 1784 Science Photo Library




Human Anatomy Neck Human Neck Anatomy Gethumananatomy Muscle Anatomy Neck Muscle Anatomy Muscle Diagram




Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And Physiology I




Cervical Dysfunction And Pain In The Head And Neck Causes And Osteopathic Options




Obliquus Capitis Inferior Muscle Wikipedia




What Muscles Cause Neck And Head Pain Physit


